Cost-effectiveness of pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy in patients with platinum-pretreated, recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer
- PMID: 38267990
- PMCID: PMC10809591
- DOI: 10.1186/s12962-024-00515-6
Cost-effectiveness of pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy in patients with platinum-pretreated, recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer
Abstract
Background: Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monoclonal antibody, pembrolizumab, is a promising drug for platinum-pretreated, recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC). We aimed to assess the cost-effectiveness of pembrolizumab compared with chemotherapy for Chinese patients in this NPC.
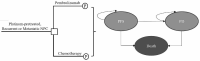
Methods: The cost-effectiveness of pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy was evaluated using a partitioned survival model with a 5-year boundary. Efficacy and toxicity data were derived from the KEYNOTE-122 trials. Economic indicators including life-years (LYs), quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs), incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER), and lifetime cost were used. One-way analysis and probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA) were performed to explore the uncertainties. Additionally, various scenario analyses, including different pembrolizumab price calculations and discount rates were performed.
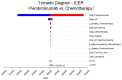
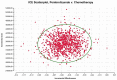
Results: Pembrolizumab or chemotherapy alone respectively yielded 2.82 QALYs (3.96 LYs) and 2.73 QALYs (3.93 LYs) with an ICER of $422,535 per QALYs ($1,232,547 per LYs). This model was primarily influenced by the price of pembrolizumab. Furthermore, PSA indicated that pembrolizumab had none probability of being cost-effective compared with chemotherapy at a willingness-to- pay (WTP) of $38223. Scenario analyses revealed that irrespective of any potential price reduction or adjustments in the discount rate, no discernible impact on the ultimate outcome was observed.
Conclusion: Pembrolizumab was less cost-effective for patients with platinum-pretreated, recurrent or metastatic NPC compared with chemotherapy in China.
Keywords: Capecitabine; Chemotherapy; Cost-effectiveness; Docetaxel; Gemcitabine; Nasopharyngeal cancer; PD-1; Pembrolizumab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of pembrolizumab for treatment of platinum-resistant recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in China: an economic analysis based on a randomised, open-label, phase III trial.BMJ Open. 2020 Dec 18;10(12):e038867. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038867. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 33371020 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of pembrolizumab monotherapy versus chemotherapy for previously untreated advanced non-small cell lung cancer.J Med Econ. 2020 Sep;23(9):952-960. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2020.1775620. Epub 2020 Jun 22. J Med Econ. 2020. PMID: 32462958 Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of pembrolizumab versus standard-of-care chemotherapy for first-line treatment of PD-L1 positive (>50%) metastatic squamous and non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer in France.Lung Cancer. 2019 Jan;127:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.11.008. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30642550
-
Pembrolizumab monotherapy versus chemotherapy in platinum-pretreated, recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer (KEYNOTE-122): an open-label, randomized, phase III trial.Ann Oncol. 2023 Mar;34(3):251-261. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.12.007. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Ann Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36535566 Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer in China.Curr Med Res Opin. 2023 Mar;39(3):433-440. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2023.2178081. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Curr Med Res Opin. 2023. PMID: 36757780
References
-
- Bossi P, Chan AT, Licitra L, Trama A, Orlandi E, Hui EP, Halamkova J, Mattheis S, Baujat B, Hardillo J, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: ESMO-EURACAN clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up(dagger) Ann Oncol. 2021;32:452–65. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.12.007. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

