Fbxw7 suppresses carcinogenesis and stemness in triple-negative breast cancer through CHD4 degradation and Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibition
- PMID: 38268032
- PMCID: PMC10809768
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-04897-2
Fbxw7 suppresses carcinogenesis and stemness in triple-negative breast cancer through CHD4 degradation and Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibition
Abstract
Background: Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a small population of cells in tumor tissues that can drive tumor initiation and promote tumor progression. A small number of previous studies indirectly mentioned the role of F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7 (FBXW7) as a tumor suppressor in Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). However, few studies have focused on the function of FBXW7 in cancer stemness in TNBC and the related mechanism.
Methods: We detected FBXW7 by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in 80 TNBC patients. FBXW7 knockdown and overexpression in MD-MBA-231 and HCC1937 cell models were constructed. The effect of FBXW7 on malignant phenotype and stemness was assessed by colony assays, flow cytometry, transwell assays, western blot, and sphere formation assays. Immunoprecipitation-Mass Spectrometry (IP-MS) and ubiquitination experiments were used to find and verify potential downstream substrate proteins of FBXW7. Animal experiments were constructed to examine the effect of FBXW7 on tumorigenic potential and cancer stemness of TNBC cells in vivo.
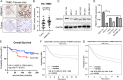
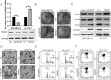
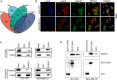
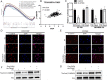
Results: The results showed that FBXW7 was expressed at low levels in TNBC tissues and positively correlated with prognosis of TNBC patients. In vitro, FBXW7 significantly inhibited colony formation, cell cycle progression, cell migration, EMT process, cancer stemness and promotes apoptosis. Further experiments confirmed that chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 4 (CHD4) is a novel downstream target of FBXW7 and is downregulated by FBXW7 via proteasomal degradation. Moreover, CHD4 could promote the nuclear translocation of β-catenin and reverse the inhibitory effect of FBXW7 on β-catenin, and ultimately activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Rescue experiments confirmed that the FBXW7-CHD4-Wnt/β-catenin axis was involved in regulating the maintenance of CSC in TNBC cells. In animal experiments, FBXW7 reduced CSC marker expression and suppressed TNBC cell tumorigenesis in vivo.
Conclusions: Taken together, these results highlight that FBXW7 degrades CHD4 protein through ubiquitination, thereby blocking the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway to inhibit the stemness of TNBC cells. Thus, targeting FBXW7 may be a promising strategy for therapeutic intervention against TNBC.
Keywords: CHD4; Fbxw7; Stemness; Triple-negative breast cancer; Wnt/β-catenin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nek2B activates the wnt pathway and promotes triple-negative breast cancer chemothezrapy-resistance by stabilizing β-catenin.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 7;38(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1231-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31174562 Free PMC article.
-
CUEDC2 Drives β-Catenin Nuclear Translocation and Promotes Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis.Cells. 2022 Sep 29;11(19):3067. doi: 10.3390/cells11193067. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231027 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals the intra-tumoral heterogeneity and SQSTM1/P62 and Wnt/β-catenin mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition and stemness of triple-negative breast cancer.Exp Cell Res. 2024 May 1;438(1):114032. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114032. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38583856
-
Modulation of Wnt/Beta-Catenin Pathway by Major Dietary Phytochemicals Against Breast Cancer Development.Biology (Basel). 2025 Feb 13;14(2):194. doi: 10.3390/biology14020194. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges for Triple Negative Breast Cancer Treatment: Defeating Heterogeneity and Cancer Stemness.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 1;14(17):4280. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174280. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulator of cullins-1 predicts a poor prognosis and regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition process through GSK-3β/Wnt signaling in renal cell carcinoma.Transl Androl Urol. 2025 Apr 30;14(4):974-985. doi: 10.21037/tau-2024-646. Epub 2025 Apr 27. Transl Androl Urol. 2025. PMID: 40376526 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin Remodulator CHD4: A Potential Target for Cancer Interception.Genes (Basel). 2025 Feb 15;16(2):225. doi: 10.3390/genes16020225. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40004553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FBXW7 in gastrointestinal cancers: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic prospects.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 18;15:1505027. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1505027. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39749199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin modification in the regulation of tumor immunotherapy resistance mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Aug 30;13(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00552-0. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39223632 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

