Deucravacitinib, an oral, selective, allosteric tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor, in Japanese patients with moderate to severe plaque, erythrodermic, or generalized pustular psoriasis: Efficacy and safety results from an open-label, phase 3 trial
- PMID: 38268101
- PMCID: PMC11483964
- DOI: 10.1111/1346-8138.17074
Deucravacitinib, an oral, selective, allosteric tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor, in Japanese patients with moderate to severe plaque, erythrodermic, or generalized pustular psoriasis: Efficacy and safety results from an open-label, phase 3 trial
Abstract
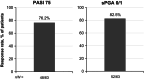
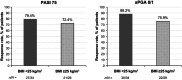
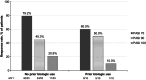
Deucravacitinib, an oral, selective, allosteric tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor, is approved in Japan for adult patients with plaque (PP), generalized pustular (GPP), and erythrodermic (EP) psoriasis who have had an inadequate response to conventional systemic therapies. This approval is based on results from the global phase 3 POETYK PSO-1 and PSO-2 trials in which deucravacitinib was associated with significantly improved efficacy outcomes compared with placebo in adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, and results described here from POETYK PSO-4, an open-label, single-arm, phase 3 trial (NCT03924427), which evaluated the efficacy and safety of deucravacitinib 6 mg once daily in adult Japanese patients with PP, GPP, or EP. The coprimary endpoints were the proportion of patients achieving a ≥75% reduction from baseline in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 75) and a static Physician's Global Assessment score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) (sPGA 0/1) with at least a two-point improvement from baseline at week 16. Nonresponder imputation was used for missing data. Efficacy responses, adverse events (AEs), and serious AEs (SAEs) were recorded for up to 52 weeks. Seventy-four patients were treated (PP, n = 63; GPP, n = 3; EP, n = 8). At week 16, 76.2%, 66.7%, and 37.5% of patients with PP, GPP, and EP, respectively, had achieved PASI 75, and 82.5%, 0.0%, and 50.0% had achieved sPGA 0/1. Responses were overall maintained through week 52. AEs occurred in 74.6% of patients with PP, 100% of patients with GPP, and 87.5% of patients with EP. The most common AEs were nasopharyngitis and acne. Rates of SAEs and discontinuations were low. There were no deaths. Deucravacitinib was effective and well tolerated in Japanese patients with moderate to severe PP and in a limited number of patients with GPP or EP.
Keywords: Asian population; clinical trial; phase 3; psoriasis; tyrosine kinase 2.
© 2024 The Authors. The Journal of Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Dermatological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
S.I. has received grants and personal fees from AbbVie, Eisai, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Leo Pharma, Maruho, Sun Pharma, Taiho Yakuhin, Tanabe Mitsubishi, and Torii Yakuhin, and has received personal fees from Amgen (Celgene), Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and UCB. Y.O. has received research grants from AbbVie, Eisai, Maruho, Shiseido, Sun Pharma, and Torii Pharmaceutical; has received honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Janssen Pharma, Jimro, Kyowa Kirin, Leo Pharma, Maruho, Novartis Pharma, Pfizer, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Tanabe‐Mitsubishi, Torii Pharmaceutical, and UCB; and has conducted clinical trials for AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Maruho, Pfizer, Sun Pharma, and UCB. Y.T. has received research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Jimro, Kyowa Kirin, Leo Pharma, Maruho, Sun Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Tanabe‐Mitsubishi, Torii Pharmaceutical, and UCB; has received honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Jimro, Kyowa Kirin, Leo Pharma, Maruho, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Tanabe‐Mitsubishi, Torii Pharmaceutical, and UCB; and has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Maruho, Novartis, Taiho Pharmaceutical, and UCB. M.O. has received honoraria and/or research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Leo Pharma, Maruho, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Nichi‐Iko, Nippon Kayaku, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Torii Pharmaceutical, and UCB. E.C., A.N., Y.S., and S.B. are employees of and shareholders in Bristol Myers Squibb. A.M. has received honoraria as meeting chair/lecturer for AbbVie, AYUMI Pharmaceutical, Boehringer Ingelheim Japan, Celgene K.K., Eisai, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Inforward, Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Kyowa Kirin, Maruho Co., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Nippon Kayaku, Novartis Pharma K.K., Taiho Pharmaceutical, Torii Pharmaceutical, and Ushio; has received funding from AbbVie GK, Eisai, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Kyowa Kirin, Leo Pharma K.K., Maruho, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Novartis Pharma K.K., Taiho Pharmaceutical, and Torii Pharmaceutical; and has received consulting fees from AbbVie GK, Boehringer Ingelheim Japan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene K.K., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., GlaxoSmithKline K.K., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Kyowa Kirin, Maruho, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Nichi‐Iko Pharmaceutical, Nippon Kayaku, Novartis Pharma K.K., Pfizer Japan, Sun Pharma, Torii Pharmaceutical, and UCB Japan. Shinichi Imafuku and Yayoi Tada are Editorial Board members of
Figures



References
-
- Tsuruta N, Imafuku S. Establishment of the Western Japan psoriasis registry and first cross‐sectional analysis of registered patients. J Dermatol. 2021;48:1709–1718. - PubMed
-
- Greb JE, Goldminz AM, Elder JT, Lebwohl MG, Gladman DD, Wu JJ, et al. Psoriasis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16082. - PubMed
-
- Saeki H, Terui T, Morita A, Sano S, Imafuku S, Asahina A, et al. Japanese guidance for use of biologics for psoriasis (the 2019 version). J Dermatol. 2020;47:201–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

