Plasma Matrix Metalloproteinase Concentrations and Risk of Interstitial Lung Disease in a Prospective Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohort
- PMID: 38268499
- PMCID: PMC11213673
- DOI: 10.1002/art.42812
Plasma Matrix Metalloproteinase Concentrations and Risk of Interstitial Lung Disease in a Prospective Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohort
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the associations of plasma matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) with prevalent and incident interstitial lung disease (ILD) in people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Within a multicenter, prospective cohort of US veterans with RA, we performed a cross-sectional study of prevalent ILD and cohort study of incident ILD. ILD diagnoses were validated by medical record review of provider diagnoses and chest imaging and/or pathology reports. MMP-1, 3, 7, and 9 concentrations were measured in plasma samples, then standardized and categorized into quartiles. The associations of MMPs with prevalent and incident ILD were assessed with logistic (prevalent) and Cox (incident) regression models adjusted for RA-ILD risk factors.
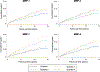
Results: Among 2,312 participants (88.9% male; mean age 63.8 years), 96 had prevalent ILD. Incident ILD developed in 130 participants over 17,378 person-years of follow-up (crude incidence rate 7.5/1,000 person-years). Participants with the highest quartile of MMP-7 concentrations had a nearly four-fold increased odds of prevalent ILD (adjusted odds ratio 3.78 [95% confidence interval (95% CI) 1.86-7.65]) and over two-fold increased risk of incident ILD (adjusted hazard ratio 2.33 [95% CI 1.35-4.02]). Higher MMP-9 concentrations were also associated with prevalent and incident ILD, as well as negatively correlated with forced vital capacity among those with prevalent ILD (r = -0.30, P = 0.005).
Conclusion: MMP-7 and MMP-9 were strongly associated with both prevalent and incident ILD in this large, multicenter RA cohort after adjustment for other RA-ILD risk factors. These population-level findings further support a potential pathogenic role for MMPs in RA-ILD and suggest that their measurement could facilitate RA-ILD risk stratification.
© 2024 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Rheumatology. This article has been contributed to by U.S. Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Peripheral Biomarker Signatures in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025 Aug;77(8):971-980. doi: 10.1002/art.43149. Epub 2025 Apr 7. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40033001
-
Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors as upcoming biomarker signatures of connective tissue diseases-related interstitial lung disease: towards an earlier and accurate diagnosis.Mol Med. 2025 Feb 20;31(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01128-2. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39979794 Free PMC article.
-
Forced vital capacity trajectories and risk of lung transplant and ILD-related mortality among patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Aug;43(8):2453-2466. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07028-w. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38898318 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclophosphamide for connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 3;1(1):CD010908. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010908.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29297205 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of abatacept in interstitial lung disease of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic literature review.Autoimmun Rev. 2021 Jun;20(6):102830. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102830. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Autoimmun Rev. 2021. PMID: 33887489
Cited by
-
A Review of Advances in Molecular Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis: From In Vitro to Clinic Applications Using Radiolabeled Targeting Vectors with Technetium-99m.Life (Basel). 2024 Jun 12;14(6):751. doi: 10.3390/life14060751. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Biomarkers of Pulmonary Damage and Risk for Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease.J Rheumatol. 2025 Apr 1;52(4):323-333. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.2024-0713. J Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39814449
-
Peripheral Biomarker Signatures in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025 Aug;77(8):971-980. doi: 10.1002/art.43149. Epub 2025 Apr 7. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40033001
-
Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: Advancing the identification and management.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2025 Feb;70S:152578. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2024.152578. Epub 2024 Nov 10. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2025. PMID: 39547863 Review.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors as upcoming biomarker signatures of connective tissue diseases-related interstitial lung disease: towards an earlier and accurate diagnosis.Mol Med. 2025 Feb 20;31(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01128-2. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39979794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duarte AC, Porter JC, Leandro MJ. The lung in a cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients-an overview of different types of involvement and treatment. Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 2019;58(11):2031–2038. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PR200793/U.S. Department of Defense
- IK2 CX002203/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- BX004660/VA Biomedical Laboratory Research and Development
- Horizon Therapeutics
- IK2 CX002351/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- CX002351/Veterans Affairs Clinical Science Research and Development (VA CSR&D)
- U54 GM115458/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004660/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- RX003644/VA Rehabilitation Research & Development
- I01 CX001703/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- CX002203/Veterans Affairs Clinical Science Research and Development (VA CSR&D)
- I01 RX003644/RX/RRD VA/United States
- CX001703/Veterans Affairs Clinical Science Research and Development (VA CSR&D)
- University of Nebraska Medical Center's Mentored Scholars Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

