Ultrasmall cerium oxide nanoparticles as highly sensitive X-ray contrast agents and their antioxidant effect
- PMID: 38268539
- PMCID: PMC10805080
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra08372a
Ultrasmall cerium oxide nanoparticles as highly sensitive X-ray contrast agents and their antioxidant effect
Abstract
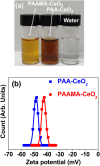
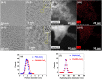
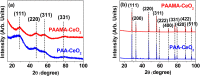
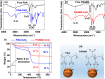
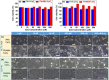
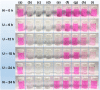
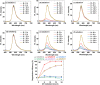
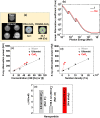
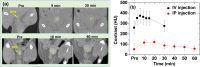
Owing to their theranostic properties, cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles have attracted considerable attention for their key applications in nanomedicine. In this study, ultrasmall CeO2 nanoparticles (particle diameter = 1-3 nm) as X-ray contrast agents with an antioxidant effect were investigated for the first time. The nanoparticles were coated with hydrophilic and biocompatible poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) and poly(acrylic acid-co-maleic acid) (PAAMA) to ensure satisfactory colloidal stability in aqueous media and low cellular toxicity. The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, dynamic light scattering, cell viability assay, photoluminescence spectroscopy, and X-ray computed tomography (CT). Their potential as X-ray contrast agents was demonstrated by measuring phantom images and in vivo CT images in mice injected intravenously and intraperitoneally. The X-ray attenuation of these nanoparticles was greater than that of the commercial X-ray contrast agent Ultravist and those of larger CeO2 nanoparticles reported previously. In addition, they exhibited an antioxidant effect for the removal of hydrogen peroxide. The results confirmed that the PAA- and PAAMA-coated ultrasmall CeO2 nanoparticles demonstrate potential as highly sensitive radioprotective or theranostic X-ray contrast agents.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Facile Synthesis and X-ray Attenuation Properties of Ultrasmall Platinum Nanoparticles Grafted with Three Types of Hydrophilic Polymers.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Feb 22;13(5):806. doi: 10.3390/nano13050806. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36903686 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrophilic Biocompatible Poly(Acrylic Acid-co-Maleic Acid) Polymer as a Surface-Coating Ligand of Ultrasmall Gd2O3 Nanoparticles to Obtain a High r1 Value and T1 MR Images.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Dec 22;11(1):2. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11010002. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33375089 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of gold-supported cerium oxide nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Nov 27;9:5515-31. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S70087. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 25473288 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasmall Europium, Gadolinium, and Dysprosium Oxide Nanoparticles: Polyol Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Imaging Applications.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020;20(17):1767-1780. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666200604163452. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32496986 Review.
-
Cerium oxide nanoparticles: Chemical properties, biological effects and potential therapeutic opportunities (Review).Biomed Rep. 2024 Jan 29;20(3):48. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1736. eCollection 2024 Mar. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 38357238 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Ultrasmall Inorganic Nanoparticles for Nanomedicine: From Diagnosis to Therapeutics.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 May 21;17(20):28982-29001. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c02810. Epub 2025 May 9. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40343711 Review.
-
Europium-doped cerium oxide nanoparticle-impregnated Hyalgan® (CartiOxgel): an intra-articular contrast agent for X-ray CT and optical imaging.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 7;15(29):23374-23395. doi: 10.1039/d5ra01830g. eCollection 2025 Jul 4. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40626062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Materón E. M. Miyazaki C. M. Carr O. Joshi N. Picciani P. H. S. Dalmaschio C. J. Davis F. Shimizu F. M. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021;6:100163.
-
- Kumar K. H. Venkatesh N. Bhowmik H. Kuila A. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018;4:3765–3775.
-
- Yu S.-B. Watson A. D. Chem. Rev. 1999;99:2353–2378. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

