Effects of OxyR regulator on oxidative stress, Apx toxin secretion and virulence of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
- PMID: 38268788
- PMCID: PMC10806198
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1324760
Effects of OxyR regulator on oxidative stress, Apx toxin secretion and virulence of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
Abstract
Introduction: Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, the causative agent of porcine pleuropneumonia, poses a significant threat to global swine populations due to its high prevalence, mortality rates, and substantial economic ramifications. Understanding the pathogen's defense mechanisms against host-produced reactive oxygen species is crucial for its survival, with OxyR, a conserved bacterial transcription factor, being pivotal in oxidative stress response.
Methods: This study investigated the presence and role of OxyR in A. pleuropneumoniae serovar 1-12 reference strains. Transcriptomic analysis was conducted on an oxyR disruption mutant to delineate the biological activities influenced by OxyR. Additionally, specific assays were employed to assess urease activity, catalase expression, ApxI toxin secretion, as well as adhesion and invasion abilities of the oxyR disruption mutant on porcine 3D4/21 and PT cells. A mice challenge experiment was also conducted to evaluate the impact of oxyR inactivation on A. pleuropneumoniae virulence.
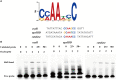
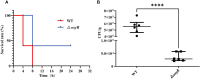
Results: OxyR was identified as a conserved regulator present in A. pleuropneumoniae serovar 1-12 reference strains. Transcriptomic analysis revealed the involvement of OxyR in multiple biological activities. The oxyR disruption resulted in decreased urease activity, elevated catalase expression, enhanced ApxI toxin secretion-attributed to OxyR binding to the apxIBD promoter-and reduced adhesion and invasion abilities on porcine cells. Furthermore, inactivation of oxyR reduced the virulence of A. pleuropneumoniae in a mice challenge experiment.
Discussion: The findings highlight the pivotal role of OxyR in influencing the virulence mechanisms of A. pleuropneumoniae. The observed effects on various biological activities underscore OxyR as an essential factor contributing to the pathogenicity of this bacterium.
Keywords: Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae; Apx toxins; oxidative stress; oxyR gene; virulence.
Copyright © 2024 Guo, Quan, Cui, Cao, Wen and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Construction and immunogenicity of an attenuated mutant of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae by insertional inactivation of apxIC].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2007 Oct;47(5):923-7. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 18062275 Chinese.
-
Molecular investigation of the role of ApxI and ApxII in the virulence of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 5.Microb Pathog. 1995 Mar;18(3):197-209. doi: 10.1016/s0882-4010(95)90049-7. Microb Pathog. 1995. PMID: 7565014
-
Isolation of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serovar 15-like strain from a field case of porcine pleuropneumonia in Japan.J Vet Med Sci. 2007 Sep;69(9):961-4. doi: 10.1292/jvms.69.961. J Vet Med Sci. 2007. PMID: 17917383
-
New trends in innovative vaccine development against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae.Vet Microbiol. 2018 Apr;217:66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.02.028. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Vet Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29615259 Review.
-
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae: The molecular determinants of virulence and pathogenesis.Adv Microb Physiol. 2021;78:179-216. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2020.12.001. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Adv Microb Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34147185 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

