[Relationship of triglyceride-glucose index and its derivatives with blood pressure abnormalities in adolescents: an analysis based on a restricted cubic spline model]
- PMID: 38269460
- PMCID: PMC10817734
- DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2306049
[Relationship of triglyceride-glucose index and its derivatives with blood pressure abnormalities in adolescents: an analysis based on a restricted cubic spline model]
Abstract
Objectives: To explore the relationship of triglyceride-glucose index (TyG), triglyceride-glucose-body mass index (TyG-BMI), and triglyceride-glucose-waist circumference index (TyG-WC) with blood pressure abnormalities in adolescents, providing theoretical basis for the prevention and control of hypertension in adolescents.
Methods: A stratified cluster sampling method was used to select 1 572 adolescents aged 12 to 18 years in Yinchuan City for questionnaire surveys, physical measurements, and laboratory tests. Logistic regression analysis and restricted cubic spline analysis were employed to examine the relationship of TyG, TyG-BMI, and TyG-WC with blood pressure abnormalities in adolescents.
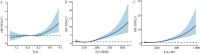
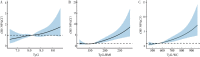
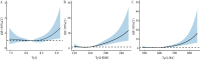
Results: Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that after adjusting for confounding factors, the groups with the highest quartile of TyG, TyG-BMI, and TyG-WC had 1.48 times (95%CI: 1.07-2.04), 3.71 times (95%CI: 2.67-5.15), and 4.07 times (95%CI: 2.89-5.73) higher risks of blood pressure abnormalities compared to the groups with the lowest quartile, respectively. Moreover, as the levels of TyG, TyG-BMI, and TyG-WC increased, the risk of blood pressure abnormalities gradually increased (P<0.05). A non-linear dose-response relationship was observed between TyG-BMI and the risk of blood pressure abnormalities (P overall trend<0.001, P non-linearity=0.002). Linear dose-response relationships were found between TyG and the risk of blood pressure abnormalities (P overall trend<0.001, P non-linearit =0.232), and between TyG-WC and the risk of blood pressure abnormalities (P overall trend<0.001, P non-linearity=0.224).
Conclusions: Higher levels of TyG and its derivatives are associated with an increased risk of blood pressure abnormalities in adolescents, with linear or non-linear dose-response relationships.
目的: 探讨青少年三酰甘油-葡萄糖指数(triglyceride-glucose index, 简称TyG)、三酰甘油-葡萄糖-体重指数(triglyceride-glucose-body mass index, 简称TyG-BMI)以及三酰甘油-葡萄糖-腰围指数(triglyceride-glucose-waist circumference index, 简称TyG-WC)与血压异常的关系,为青少年高血压的防控提供理论依据。方法: 通过分层整群抽样的方法抽取银川市1 572例12~18岁青少年进行问卷调查、体格测量和实验室检测,通过logistic回归分析模型结合限制性立方样条分析青少年TyG、TyG-BMI、TyG-WC与血压异常的关系。结果: 多因素logistic回归分析显示,校正混杂因素后,TyG、TyG-BMI、TyG-WC最高四分位数组发生血压异常的风险分别为最低四分位数组的1.48倍(95%CI:1.07~2.04)、3.71倍(95%CI:2.67~5.15)和4.07倍(95%CI:2.89~5.73);且随着TyG、TyG-BMI和TyG-WC水平升高,血压异常风险逐渐增加(P<0.05)。TyG-BMI与血压异常风险之间存在非线性剂量-反应关系(P 总趋势<0.001,P 非线性=0.002);TyG(P 总趋势<0.001,P 非线性=0.232)、TyG-WC(P 总趋势<0.001,P 非线性=0.224)均与血压异常风险之间存在线性剂量-反应关系。结论: TyG及其衍生指数水平升高可增加青少年发生血压异常的风险,且与血压异常风险之间存在线性或非线性剂量-反应关系。.
Keywords: Adolescent; Blood pressure; Triglyceride-glucose index; Triglyceride-glucose-body mass index; Triglyceride-glucose-waist circumference index.
Conflict of interest statement
所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between the combination of the triglyceride-glucose index and obesity-related indices with hyperuricemia among children and adolescents in China.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Apr 23;24(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02547-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40269945 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and its combined obesity indicators and the risk of hypertension in middle-aged and older Chinese adults: A nationwide cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 2;20(1):e0316581. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316581. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39746074 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and hypertension risk: evidence from a cross-sectional study with 60,283 adults in eastern China.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 May 23;24(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03934-8. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38783200 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the triglyceride-glucose index and its related parameters with frailty.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 May 21;23(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02147-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38773587 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between lipid levels, TyG, TyG-BMI index and hypertension in Tibetan population in Tibet, China based on restricted cubic spline model.BMC Public Health. 2024 Dec 27;24(1):3595. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-21160-x. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39731090 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

