The defect feature extraction of ultrasonic phased array detection based on adaptive region growth
- PMID: 38271344
- PMCID: PMC10810511
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297206
The defect feature extraction of ultrasonic phased array detection based on adaptive region growth
Abstract
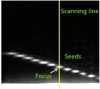
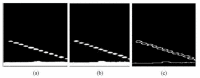
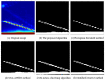
An ultrasonic phased array defect extraction method based on adaptive region growth is proposed, aiming at problems such as difficulty in defect identification and extraction caused by noise interference and complex structure of the detected object during ultrasonic phased array detection. First, bilateral filtering and grayscale processing techniques are employed for the purpose of noise reduction and initial data processing. Following this, the maximum sound pressure within the designated focusing region serves as the seed point. An adaptive region iteration method is subsequently employed to execute automatic threshold capture and region growth. In addition, mathematical morphology is applied to extract the processed defect features. In the final stage, two sets of B-scan images depicting hole defects of varying sizes are utilized for experimental validation of the proposed algorithm's effectiveness and applicability. The defect features extracted through this algorithm are then compared and analyzed alongside the histogram threshold method, Otsu method, K-means clustering algorithm, and a modified iterative method. The results reveal that the margin of error between the measured results and the actual defect sizes is less than 13%, representing a significant enhancement in the precision of defect feature extraction. Consequently, this method establishes a dependable foundation of data for subsequent tasks, such as defect localization and quantitative and qualitative analysis.
Copyright: © 2024 Wang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Defect Detection Algorithm for Wing Skin with Stiffener Based on Phased-Array Ultrasonic Imaging.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 21;23(13):5788. doi: 10.3390/s23135788. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37447636 Free PMC article.
-
Laser ultrasonic imaging of complex defects with full-matrix capture and deep-learning extraction.Ultrasonics. 2023 Mar;129:106915. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2022.106915. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Ultrasonics. 2023. PMID: 36584656
-
Ultrasonic Phased Array Testing and Identification of Multiple-Type Internal Defects in Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics Based on Convolutional Neural Network.Materials (Basel). 2025 Jan 12;18(2):318. doi: 10.3390/ma18020318. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39859789 Free PMC article.
-
Transcranial Ultrasonic Focusing by a Phased Array Based on Micro-CT Images.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Dec 8;23(24):9702. doi: 10.3390/s23249702. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139547 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced approach to fusing automatic characteristic frequency extraction and adaptive array signals weighting for abnormal machine sound localization.ISA Trans. 2024 Feb;145:443-467. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2023.11.041. Epub 2023 Dec 1. ISA Trans. 2024. PMID: 38052708
References
-
- Yuan C, Xie C, Li L, Zhang F, Gubanski SM. Ultrasonic phased array detection of internal defects in composite insulators. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul. 2016;23: 525–31. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2015.005225 - DOI
-
- Tiwari KA, Raisutis R, Tumsys O, Ostreika A, Jankauskas K, Jakutavicius J. Defect estimation in non-destructive testing of composites by ultrasonic guided waves and image processing. Electronics. 2019;8: 315. doi: 10.3390/electronics8030315 - DOI
-
- Siljama O, Koskinen T, Jessen-Juhler O, Virkkunen I. Automated flaw detection in multi-channel phased array ultrasonic data using machine learning. J Nondestruct Eval. 2021;40: 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s10921-021-00796-4 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

