Weighting Low-Intensity MS/MS Ions and m/ z Frequency for Spectral Library Annotation
- PMID: 38271611
- PMCID: PMC10854760
- DOI: 10.1021/jasms.3c00353
Weighting Low-Intensity MS/MS Ions and m/ z Frequency for Spectral Library Annotation
Abstract
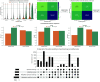
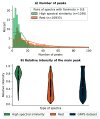
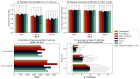
Calculating spectral similarity is a fundamental step in MS/MS data analysis in untargeted metabolomics experiments, as it facilitates the identification of related spectra and the annotation of compounds. To improve matching accuracy when querying an experimental mass spectrum against a spectral library, previous approaches have proposed increasing peak intensities for high m/z ranges. These high m/z values tend to be smaller in magnitude, yet they offer more crucial information for identifying the chemical structure. Here, we evaluate the impact of using these weights for identifying structurally related compounds and mass spectral library searches. Additionally, we propose a weighting approach that (i) takes into account the frequency of the m/z values within a spectral library in order to assign higher importance to the most common peaks and (ii) increases the intensity of lower peaks, similar to previous approaches. To demonstrate our approach, we applied weighting preprocessing to modified cosine, entropy, and fidelity distance metrics and benchmarked it against previously reported weights. Our results demonstrate how weighting-based preprocessing can assist in annotating the structure of unknown spectra as well as identifying structurally similar compounds. Finally, we examined scenarios in which the utilization of weights resulted in diminished performance, pinpointing spectral features where the application of weights might be detrimental.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): P.C.D. is an advisor and holds equity in Cybele and a Scientific co-founder, holds equity in and is an advisor to Ometa, Enveda, and Arome with prior approval by UC-San Diego. All other authors were employees of Enveda Biosciences Inc. during the course of this work and have a real or potential ownership interest in Enveda Biosciences Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Alseekh S.; Aharoni A.; Brotman Y.; Contrepois K.; D’Auria J.; Ewald J.; C Ewald J.; Fraser P. D.; Giavalisco P.; Hall R. D.; Heinemann M.; Link H.; Luo J.; Neumann S.; Nielsen J.; Perez de Souza L.; Saito K.; Sauer U.; Schroeder F. C.; Schuster S.; Siuzdak G.; Skirycz A.; Sumner L. W.; Snyder M. P.; Tang H.; Tohge T.; Wang Y.; Wen W.; Wu S.; Xu G.; Zamboni N.; Fernie A. R. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: a guide for annotation, quantification and best reporting practices. Nat. Methods 2021, 18 (7), 747–756. 10.1038/s41592-021-01197-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bittremieux W.; Schmid R.; Huber F.; van der Hooft J. J. J.; Wang M.; Dorrestein P. C. Comparison of cosine, modified cosine, and neutral loss based spectrum alignment for discovery of structurally related molecules. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 33 (9), 1733–1744. 10.1021/jasms.2c00153. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

