The role of RNA epigenetic modification-related genes in the immune response of cattle to mastitis induced by Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 38271969
- PMCID: PMC11222847
- DOI: 10.5713/ab.23.0323
The role of RNA epigenetic modification-related genes in the immune response of cattle to mastitis induced by Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
Objective: RNA epigenetic modifications play an important role in regulating immune response of mammals. Bovine mastitis induced by Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a threat to the health of dairy cattle. There are numerous RNA modifications, and how these modification-associated enzymes systematically coordinate their immunomodulatory effects during bovine mastitis is not well reported. Therefore, the role of common RNA modificationrelated genes (RMRGs) in bovine S. aureus mastitis was investigated in this study.
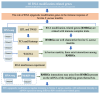
Methods: In total, 80 RMRGs were selected for this study. Four public RNA-seq data sets about bovine S. aureus mastitis were collected and one additional RNA-seq data set was generated by this study. Firstly, quantitative trait locus (QTL) database, transcriptome-wide association studies (TWAS) database and differential expression analyses were employed to characterize the potential functions of selected enzyme genes in bovine S. aureus mastitis. Correlation analysis and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) were used to further investigate the relationships of RMRGs from different types at the mRNA expression level. Interference experiments targeting the m6A demethylase FTO and utilizing public MeRIP-seq dataset from bovine Mac-T cells were used to investigate the potential interaction mechanisms among various RNA modifications.
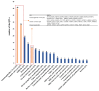
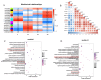
Results: Bovine QTL and TWAS database in cattle revealed associations between RMRGs and immune-related complex traits. S. aureus challenged and control groups were effectively distinguished by principal component analysis based on the expression of selected RMRGs. WGCNA and correlation analysis identified modules grouping different RMRGs, with highly correlated mRNA expression. The m6A modification gene FTO showed significant effects on the expression of m6A and other RMRGs (such as NSUN2, CPSF2, and METTLE), indicating complex co-expression relationships among different RNA modifications in the regulation of bovine S. aureus mastitis.
Conclusion: RNA epigenetic modification genes play important immunoregulatory roles in bovine S. aureus mastitis, and there are extensive interactions of mRNA expression among different RMRGs. It is necessary to investigate the interactions between RNA modification genes regulating complex traits in the future.
Keywords: Mastitis; RNA Modification Gene; RNA-seq; Staphylococcus aureus.
Conflict of interest statement
We certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Becker K, Schaumburg F, Kearns A, et al. Implications of identifying the recently defined members of the Staphylococcus aureus complex S. argenteus and S. schweitzeri: a position paper of members of the ESCMID Study Group for Staphylococci and Staphylococcal Diseases (ESGS) Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019;25:1064–70. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.02.028. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

