Effects of dexmedetomidine combined with etomidate on postoperative cognitive function in older patients undergoing total intravenous anaesthesia: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial
- PMID: 38273248
- PMCID: PMC10809642
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-024-04726-7
Effects of dexmedetomidine combined with etomidate on postoperative cognitive function in older patients undergoing total intravenous anaesthesia: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Etomidate has been advocated for anesthesia in older and critically ill patients because of its hemodynamic stability. Clinical studies have shown that dexmedetomidine has neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties and improves postoperative cognitive dysfunction in older patients. The present study was to evaluate the effects of the combination of etomidate and dexmedetomidine with different anaesthesia time on postoperative cognitive function in older patients.
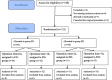
Methods: A total of 132 older patients undergoing ureteroscopic holmium laser lithotripsy were randomly divided into EN group and ED group equally. Patients whose surgery time was less than or equal to 1 h in each group were allocated to short-time surgery group (EN1 group and ED1 group), and whose surgery time was more than 1h were allocated to long-term surgery group (EN2 group and ED2 group). The primary outcome was the score of the Mini-Mental State Examination. The secondary outcomes were State-Trait Anxiety Inventory scores, Riker sedation agitation scores, Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale scores, the memory span for Arabic numerals, the plasma concentrations of S-100 calcium-binding protein B and neuron specific enolase, the time to spontaneous respiration, recovery, and extubation.
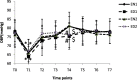
Results: The MMSE scores at t2-3 were higher in ED1 and ED2 groups than in EN1 and EN2 groups (p<0.05). Compared with ED1 and ED2 groups, the ZSDS scores, the S-AI scores and the T-AI scores at t1-2 were higher in EN1 and EN2 groups (p<0.05), respectively. The recalled Arabic numbers at t1-3 were higher in ED2 group than in EN2 group (p<0.05). The plasma concentration of S-100β at t1-2 in EN1 group and t1-3 in EN2 group were higher than that in ED1 and ED2 groups (p<0.05), respectively. Compared with ED1 and ED2 groups, the plasma concentrations of NSE were higher at t1-3 in EN1 group and t1-4 in EN2 group (p<0.05), respectively.
Conclusion: The administration of dexmedetomidine could improve postoperative cognitive dysfunction, emergence agitation, depression and anxiety, attenuate the plasma concentrations of S-100β and NSE in older patients undergoing total intravenous anaesthesia with etomidate.
Trial registration: Registration number: ChiCTR1800015421, Date: 29/03/2018.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Dexmedetomidine; Older patients; Postoperative cognitive dysfunction; etomidate.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effects of remifentanil-propofol combined with dexmedetomidine on cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients after ureteroscopic holmium laser lithotripsy: a double-blind randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2022 Mar 3;23(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06121-2. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35241145 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of etomidate combined with dexmedetomidine on adrenocortical function in elderly patients: a double-blind randomized controlled trial.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 19;12(1):12296. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16679-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35853975 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The optimal dose of dexmedetomidine as a 0.59% ropivacaine adjuvant for epidural anesthesia in great saphenous varicose vein surgery, based on hemodynamics and anesthesia efficacy: a randomized, controlled, double-blind clinical trial.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 24;11:1426512. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1426512. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39114828 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dexmedetomidine at different dosages on perioperative haemodynamics and postoperative recovery quality in elderly patients undergoing hip replacement surgery under general anaesthesia: a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2023 Jun 8;24(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07384-z. Trials. 2023. PMID: 37291651 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Application of dexmedetomidine combined with propofol-etomidate mixture in radical gastrectomy under general anesthesia.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 1;103(44):e39669. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039669. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39496064 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
The Role of Cytokines in Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorders: A Review in the Context of Anesthetic Care.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 18;13(2):506. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020506. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Midazolam and Dexmedetomidine on Cognitive Dysfunction Following Open-Heart Surgery: A Comprehensive Review.Brain Behav. 2025 Apr;15(4):e70421. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70421. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40200828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antianxiety effects of dexmedetomidine: systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2025 May 15. doi: 10.1007/s00406-025-02017-9. Online ahead of print. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40372453
-
Effects of dexmedetomidine on early postoperative cognitive function and postoperative inflammatory response: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Aug 12;15:1422049. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1422049. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39188709 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of volatile and intravenous anesthetics on postoperative cognitive dysfunction: a mechanistic review.J Anesth. 2025 Jul 16. doi: 10.1007/s00540-025-03551-5. Online ahead of print. J Anesth. 2025. PMID: 40668243 Review.
References
-
- Matchett G, Gasanova I, Riccio CA, Nasir D, Sunna MC, Bravenec BJ, et al; EvK Clinical Trial Collaborators. Etomidate versus ketamine for emergency endotracheal intubation: a randomized clinical trial. Intensive Care Med. 2022; 48(1):78-91. 10.1007/s00134-021-06577-x. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

