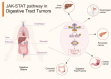
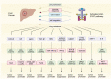
The oncogenic mechanisms of the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway in digestive tract tumors
- PMID: 38273295
- PMCID: PMC10809652
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-023-01421-9
The oncogenic mechanisms of the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway in digestive tract tumors
Abstract
Digestive tract tumors are heterogeneous and involve the dysregulation of multiple signaling pathways. The Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway plays a notable role in the oncogenesis of digestive tract tumors. Typically activated by pro-inflammatory cytokines, it regulates important biological processes, such as cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, immune responses, and inflammation. The aberrant activation of this pathway manifests in different forms, including mutations in JAKs, overexpression of cytokine receptors, and sustained STAT activation, and contributes to promoting the malignant characteristics of cancer cells, including uncontrolled proliferation, resistance to apoptosis, enhanced invasion and metastasis, angiogenesis, acquisition of stem-like properties, and drug resistance. Numerous studies have shown that aberrant activation of the JAK-STAT pathway is closely related to the development and progression of digestive tract tumors, contributing to tumor survival, angiogenesis, changes in the tumor microenvironment, and even immune escape processes. In addition, this signaling pathway also affects the sensitivity of digestive tract tumors to chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Therefore, it is crucial to comprehensively understand the oncogenic mechanisms underlying the JAK-STAT pathway in order to develop effective therapeutic strategies against digestive tract tumors. Currently, several JAK-STAT inhibitors are undergoing clinical and preclinical trials as potential treatments for various human diseases. However, further investigation is required to determine the role of this pathway, as well as the effectiveness and safety of its inhibitors, especially in the context of digestive tract tumors. In this review, we provide an overview of the structure, classic activation, and negative regulation of the JAK-STAT pathway. Furthermore, we discuss the pathogenic mechanisms of JAK-STAT signaling in different digestive tract tumors, with the aim of identifying potential novel therapeutic targets. Video Abstract.
Keywords: Biological functions; Digestive tract tumors; JAK; Oncogenic mechanism; STAT.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular dissection of Janus kinases as drug targets for inflammatory diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 8;13:1075192. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1075192. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36569926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Unraveling Signaling Complexity and Therapeutic Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 6;24(18):13764. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813764. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and therapeutic prospect of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in liver cancer.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jan;480(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-04983-5. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38519710 Review.
-
[Research Advances of JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019 Jan 20;22(1):45-51. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2019.01.09. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30674393 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Mar;80:106210. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106210. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31972425 Review.
Cited by
-
A genetic variant in the TAPBP gene enhances cervical cancer susceptibility by increasing m6A modification.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Oct;98(10):3425-3438. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03820-4. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38992170
-
Deep insight into cytokine storm: from pathogenesis to treatment.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Apr 16;10(1):112. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02178-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40234407 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources