Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- PMID: 38273791
- PMCID: PMC10995484
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0128
Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Abstract
Backgruound: We investigated the long-term efficacy and safety of initial triple therapy using metformin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods: We enrolled 170 drug-naïve patients with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level >7.5% who had started triple therapy (metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin). Glycemic, metabolic, and urinary parameters were measured for 24 months.
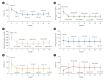
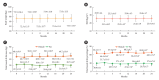
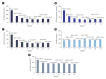
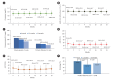
Results: After 24 months, HbA1c level decreased significantly from 11.0%±1.8% to 7.0%±1.7%. At 12 and 24 months, the rates of achievement of the glycemic target goal (HbA1c <7.0%) were 72.5% and 61.7%, respectively, and homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function and insulin resistance indices improved. Whole-body fat percentage decreased by 1.08%, and whole-body muscle percentage increased by 0.97% after 24 months. Fatty liver indices and albuminuria improved significantly. The concentration of ketone bodies was elevated at the baseline but decreased after 24 months. There were no serious adverse events, including ketoacidosis.
Conclusion: Initial triple combination therapy with metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin led to achievement of the glycemic target goal, which was maintained for 24 months without severe hypoglycemia but with improved metabolic function and albuminuria. This combination therapy may be a good strategy for drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors; Glycated hemoglobin; Sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Comment in
-
Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients (Diabetes Metab J 2024;48:253-64).Diabetes Metab J. 2024 Sep;48(5):1005-1007. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0417. Epub 2024 Sep 1. Diabetes Metab J. 2024. PMID: 39313233 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients (Diabetes Metab J 2024;48:253-64).Diabetes Metab J. 2024 Sep;48(5):1012-1013. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0485. Epub 2024 Sep 1. Diabetes Metab J. 2024. PMID: 39313235 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-Year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1577–89. - PubMed
-
- Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:580–91. - PubMed
-
- Cersosimo E, Johnson EL, Chovanes C, Skolnik N. Initiating therapy in patients newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes: combination therapy vs a stepwise approach. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20:497–507. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

