A randomized, double-blind study on the safety and immunogenicity of rTSST-1 variant vaccine: phase 2 results
- PMID: 38274114
- PMCID: PMC10808908
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102404
A randomized, double-blind study on the safety and immunogenicity of rTSST-1 variant vaccine: phase 2 results
Abstract
Background: Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) is a superantigen produced by Staphylococcus aureus that causes the life-threatening toxic shock syndrome. The development of a safe and immunogenic vaccine against TSST-1 remains an unmet medical need. We investigated the safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of a recombinant TSST-1 variant vaccine (rTSST-1v) after 1-3 injections in healthy volunteers.
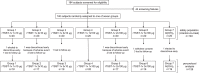
Methods: In this randomised, double-blind, adjuvant-controlled, parallel-group, phase 2 trial, healthy adults aged 18-64 were randomly allocated to undergo 1-3 injections of either 10 or 100 μg rTSST-1v or Al(OH)3. The primary endpoint was safety and tolerability of rTSST-1v in the intention-to-treat population. The per-protocol population was used for the immunogenicity analysis. The trial is registered with EudraCT#: 2015-003714-24; ClinicalTrials.gov#: NCT02814708.
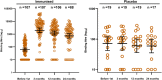
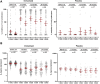
Findings: Between April and November 2017,140 subjects were enrolled and 126 completed the trial. rTSST-1v showed a good safety and tolerability profile. A total of 855 systemic adverse events occurred, 280 of which were suspected related adverse events, without dose dependency. Two participants were discontinued early because of allergic reactions. Seroconversion occurred in >81% of subjects within 3 months of the first immunisation which was sustained until 18 months after the third immunisation in over 70% of subjects in the pooled low-dose group and in over 85% in the pooled high-dose group.
Interpretation: rTSST-1v in cumulative doses of up to 300 μg was safe, well-tolerated and highly immunogenic. Two immunisations with 100 μg rTSST-1v provided the most persistent immune response and may be evaluated in future trials.
Funding: Biomedizinische Forschung & Bio-Produkte AG funded this study.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; Superantigen; TSST-1; Toxic shock syndrome; Vaccine.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
GG, CS, CF, MMS, NB, UD, AT, and BJ declare no competing interests. Martha M. Eibl was the owner of Biomedizinische Forschung & Bio-Produkte AG. DH, LS, NM, and AR are employees of the study funder Biomedizinische Forschung & Bio-Produkte AG, a biotechnology company engaged in the development of BioMed rTSST-1v.
Figures

References
-
- Davis J.P., Chesney P.J., Wand P.J., LaVenture M. Toxic-shock syndrome: epidemiologic features, recurrence, risk factors, and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1980;303(25):1429–1435. - PubMed
-
- Burnham J.P., Kollef M.H. Understanding toxic shock syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41(9):1707–1710. - PubMed
-
- Berger S., Kunerl A., Wasmuth S., Tierno P., Wagner K., Brugger J. Menstrual toxic shock syndrome: case report and systematic review of the literature. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019;19(9):e313–e321. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

