DNAJC8: a prognostic marker and potential therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38274804
- PMCID: PMC10808467
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1289548
DNAJC8: a prognostic marker and potential therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of liver cancer, accounting for ~90% of the total cases. DnaJ heat shock protein family member C8 (DNAJC8), belonging to the heat shock protein 40 (HSP40) family, is known to regulate cancer biology function. However, the role of DNAJC8 on HCC development remains unknown.
Methods: The Cancer Genome Atlas, GTEx, cBioPortal, and Human Protein Atlas were used to analyze the expression and clinical significance of DNAJC8 in HCC. Two HCC cell lines, MHCC-97H and Huh-7, were utilized to determine the biological function of DNAJC8.
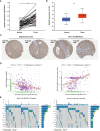
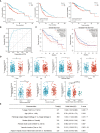
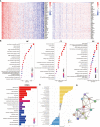
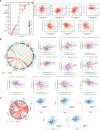
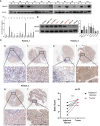
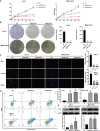
Results: DNAJC8 expression was upregulated in HCC tissues and correlated with poor clinical prognosis. It was closely related to spliceosome, nucleocytoplasmic transport, and cell cycle and might be involved in the formation of tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment. Knockdown of DNAJC8 severely inhibited HCC cell proliferation and induced apoptosis.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrate that DNAJC8 functions as an oncogene in HCC and hence may be used as a potential therapeutic target and prognostic marker for HCC.
Keywords: DNAJC8; apoptosis; bioinformatics analysis; hepatocellular carcinoma; tumor immune microenvironment.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Ju, Tang, He and Hua.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased expression of cathepsin L: a novel independent prognostic marker of worse outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 10;9(11):e112136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112136. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25384089 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM52 up-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells promotes proliferation, migration and invasion through the ubiquitination of PPM1A.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jun 13;37(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0780-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29898761 Free PMC article.
-
Over-expression of cathepsin B in hepatocellular carcinomas predicts poor prognosis of HCC patients.Mol Cancer. 2016 Feb 20;15:17. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0503-9. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26896959 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Upregulated DNA Replication and Sister Chromatid Cohesion 1 Expression on Proliferation and Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Dec 5;131(23):2827-2835. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.246076. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 30511685 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA PCAT6 predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes proliferation through the regulation of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.Cell Biochem Funct. 2020 Oct;38(7):895-904. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3510. Epub 2020 Feb 16. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020. PMID: 32064636
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

