Unlocking Early Cancer Detection: Exploring Biomarkers, Circulating DNA, and Innovative Technological Approaches
- PMID: 38274938
- PMCID: PMC10808885
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.51090
Unlocking Early Cancer Detection: Exploring Biomarkers, Circulating DNA, and Innovative Technological Approaches
Abstract
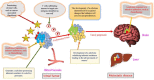
Research and development improvements in early cancer diagnosis have had a significant positive impact on health. In the treatment and prevention of cancer, early detection is essential. In this context, biomarkers are essential because they offer important information on the state of cells at any particular time. Cells go through unique changes when they shift from a healthy condition to a malignant state, changes that appropriate biomarkers may pick up. Recent advancements have been made to identify and characterize circulating cancer-specific mutations in cell-free circulating DNA derived from tumors and tumor cells. A patient's delay between the time they first detect symptoms and the time they contact a doctor has been noted for many cancer forms. The tumor's location and features significantly impact the presentation of symptoms judged appropriate for early diagnosis. Lack of knowledge of the severity of the symptoms may be one cause for this delay. Our review is largely focused on the ongoing developments of early diagnosis in the study of biomarkers, circulating DNA for diagnosis, the biology of early challenges, early symptoms, liquid biopsies, detectable by imaging, established tumor markers, plasma DNA technologies, gender differences, and artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnosis. This review aims to determine and evaluate Indicators for detecting early cancer, assessing medical conditions, and evaluating potential risks. For Individuals with a heightened likelihood of developing cancer or who have already been diagnosed, early identification is crucial for enhancing prognosis and raising the likelihood of effective treatment.
Keywords: biomarkers; biopsy; cancer; early detection; early symptoms.
Copyright © 2023, Prasanth et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Socioeconomic deprivation and survival outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer. Yu KX, Yuan WJ, Huang CH, et al. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8899994/ Am J Cancer Res. 2022;12:829–838. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
