Tempo and mode of gene expression evolution in the brain across primates
- PMID: 38275218
- PMCID: PMC10876213
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.70276
Tempo and mode of gene expression evolution in the brain across primates
Abstract
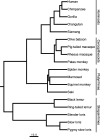
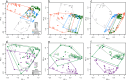
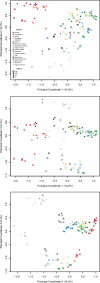
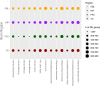
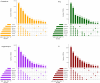
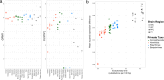
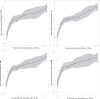
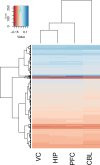
Primate evolution has led to a remarkable diversity of behavioral specializations and pronounced brain size variation among species (Barton, 2012; DeCasien and Higham, 2019; Powell et al., 2017). Gene expression provides a promising opportunity for studying the molecular basis of brain evolution, but it has been explored in very few primate species to date (e.g. Khaitovich et al., 2005; Khrameeva et al., 2020; Ma et al., 2022; Somel et al., 2009). To understand the landscape of gene expression evolution across the primate lineage, we generated and analyzed RNA-seq data from four brain regions in an unprecedented eighteen species. Here, we show a remarkable level of variation in gene expression among hominid species, including humans and chimpanzees, despite their relatively recent divergence time from other primates. We found that individual genes display a wide range of expression dynamics across evolutionary time reflective of the diverse selection pressures acting on genes within primate brain tissue. Using our samples that represent a 190-fold difference in primate brain size, we identified genes with variation in expression most correlated with brain size. Our study extensively broadens the phylogenetic context of what is known about the molecular evolution of the brain across primates and identifies novel candidate genes for the study of genetic regulation of brain evolution.
Keywords: brain; chromosomes; cis-regulation; evolutionary biology; gene expression; human; human evolution.
© 2024, Rickelton et al.
Conflict of interest statement
KR, TZ, JP, EM, JE, MR, WH, PH, CS, AB, CB No competing interests declared
Figures



Update of
References
-
- Azevedo FAC, Carvalho LRB, Grinberg LT, Farfel JM, Ferretti REL, Leite REP, Jacob Filho W, Lent R, Herculano-Houzel S. Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human brain an isometrically scaled-up primate brain. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 2009;513:532–541. doi: 10.1002/cne.21974. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bagot RC, Cates HM, Purushothaman I, Lorsch ZS, Walker DM, Wang J, Huang X, Schlüter OM, Maze I, Peña CJ, Heller EA, Issler O, Wang M, Song WM, Stein JL, Liu X, Doyle MA, Scobie KN, Sun HS, Neve RL, Geschwind D, Dong Y, Shen L, Zhang B, Nestler EJ. Circuit-wide transcriptional profiling reveals brain region-specific gene networks regulating depression susceptibility. Neuron. 2016;90:969–983. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.04.015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

