Aptasensors Based on Non-Enzymatic Peroxidase Mimics: Current Progress and Challenges
- PMID: 38275302
- PMCID: PMC10813519
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14010001
Aptasensors Based on Non-Enzymatic Peroxidase Mimics: Current Progress and Challenges
Abstract
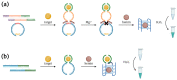
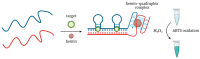
Immunoassays based on antibodies as recognizing elements and enzymes as signal-generating modules are extensively used now in clinical lab diagnostics, food, and environmental analyses. However, the application of natural enzymes and antibodies has some drawbacks, such as relatively high manufacturing costs, thermal instability, and lot-to-lot variations that lower the reproducibility of results. Oligonucleotide aptamers are able to specifically bind their targets with high affinity and selectivity, so they represent a prospective alternative to protein antibodies for analyte recognition. Their main advantages include thermal stability and long shelf life, cost-efficient chemical synthesis, and negligible batch-to-batch variations. At the same time, a wide variety of non-protein peroxidase mimics are now available that show strong potential to replace protein enzymes. Here, we review and analyze non-protein biosensors that represent a nexus of these two concepts: aptamer-based sensors (aptasensors) with optical detection (colorimetric, luminescent, or fluorescent) based on different peroxidase mimics, such as DNAzymes, nanoparticles, or metal-organic frameworks.
Keywords: aptamers; aptasensors; metal-organic frameworks; nanozymes; peroxidase mimics; peroxidase-like DNAzyme.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
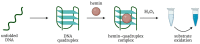


References
-
- Hosseini S., Vázquez-Villegas P., Rito-Palomares M., Martinez-Chapa S.O. SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2018. General overviews on applications of ELISA; pp. 19–29. - DOI
-
- Hosseini S., Marco P.V.-V., Sergio R.-P., Martinez-Chapa O. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): From A to Z. Springer Briefs in Applied Sciences and Technology Forensic and Medical Bioinformatics; Singapore: 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

