Reagentless Vis-NIR Spectroscopy Point-of-Care for Feline Total White Blood Cell Counts
- PMID: 38275306
- PMCID: PMC11154536
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14010053
Reagentless Vis-NIR Spectroscopy Point-of-Care for Feline Total White Blood Cell Counts
Abstract
Spectral point-of-care technology is reagentless with minimal sampling (<10 μL) and can be performed in real-time. White blood cells are non-dominant in blood and in spectral information, suffering significant interferences from dominant constituents such as red blood cells, hemoglobin and billirubin. White blood cells of a bigger size can account for 0.5% to 22.5% of blood spectra information. Knowledge expansion was performed using data augmentation through the hybridization of 94 real-world blood samples into 300 synthetic data samples. Synthetic data samples are representative of real-world data, expanding the detailed spectral information through sample hybridization, allowing us to unscramble the spectral white blood cell information from spectra, with correlations of 0.7975 to 0.8397 and a mean absolute error of 32.25% to 34.13%; furthermore, we achieved a diagnostic efficiency between 83% and 100% inside the reference interval (5.5 to 19.5 × 109 cell/L), and 85.11% for cases with extreme high white blood cell counts. At the covariance mode level, white blood cells are quantified using orthogonal information on red blood cells, maximizing sensitivity and specificity towards white blood cells, and avoiding the use of non-specific natural correlations present in the dataset; thus, the specifity of white blood cells spectral information is increased. The presented research is a step towards high-specificity, reagentless, miniaturized spectral point-of-care hematology technology for Veterinary Medicine.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; point-of-care; spectroscopy; white blood cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


 ) low WBCs, (
) low WBCs, ( ) high WBC examples, and (
) high WBC examples, and ( ) RBC Hgb major inteference bands (539–576 nm); (b) PCA scores of hemogram counts; and (c) Cell packing, scattering and WBC absorbance effects and impact on observed spectra; (d) PLS scores of blood spectra—translating maximum covariance to WBCs, where • SSD blood samples, • RWD blood samples, • low WBCs and • high WBCs and → hemogram PCA loadings and main gradient direction in PLS scores space.
) RBC Hgb major inteference bands (539–576 nm); (b) PCA scores of hemogram counts; and (c) Cell packing, scattering and WBC absorbance effects and impact on observed spectra; (d) PLS scores of blood spectra—translating maximum covariance to WBCs, where • SSD blood samples, • RWD blood samples, • low WBCs and • high WBCs and → hemogram PCA loadings and main gradient direction in PLS scores space.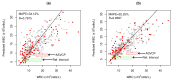
 ) represents the WBC reference interval for cats (5.5–19.5 ×
) represents the WBC reference interval for cats (5.5–19.5 ×  ) represents the ASVCP total allowable error tolerance for high WBC diagnosis.
) represents the ASVCP total allowable error tolerance for high WBC diagnosis.
 ) and quantitative (
) and quantitative ( ) results; (b) MAPE benchmarks where (
) results; (b) MAPE benchmarks where ( ) represents the ASVCP TAE for WBCs (21.45%); and (c) POC WBC diagnostic capacity: (
) represents the ASVCP TAE for WBCs (21.45%); and (c) POC WBC diagnostic capacity: ( ) percentage of correct diagnoses within WBC value interval, (– –) accumulated percentage of correct diagnosis, (
) percentage of correct diagnoses within WBC value interval, (– –) accumulated percentage of correct diagnosis, ( ) WBC histogram distibution; and RI for WBC (
) WBC histogram distibution; and RI for WBC ( ) and (
) and ( ) TAE diagnosis error tolerance.
) TAE diagnosis error tolerance.
 low and
low and  high CovM), (
high CovM), ( ) and (
) and ( ) major and minor RBC/Hgb interference bands; (c,e) high and low CovM sample spectra and corresponding used ROIs to quantify WBCs; (d,f) prediction plot for high and low CovMs.
) major and minor RBC/Hgb interference bands; (c,e) high and low CovM sample spectra and corresponding used ROIs to quantify WBCs; (d,f) prediction plot for high and low CovMs.Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the veterinary application of a point-of-care device measuring white blood cell counts.Vet J. 2012 Oct;194(1):124-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2012.03.005. Epub 2012 Apr 12. Vet J. 2012. PMID: 22503717
-
Validation of the Sysmex XT-2000iV hematology system for dogs, cats, and horses. I. Erythrocytes, platelets, and total leukocyte counts.Vet Clin Pathol. 2009 Jun;38(2):163-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-165X.2009.00125.x. Epub 2009 Apr 6. Vet Clin Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19392763
-
Validation of the Celltac alpha automated hematology analyzer for canine and feline blood samples.Vet Clin Pathol. 2013 Mar;42(1):11-8. doi: 10.1111/vcp.12019. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Vet Clin Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23278503
-
Evaluation of canine and feline leukocyte differential counts obtained with the scil vCell 5 compared to the Advia 2120 hematology analyzer and a manual method.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2023 Nov;35(6):679-697. doi: 10.1177/10406387231187899. Epub 2023 Aug 23. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2023. PMID: 37612877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histograms of Complete Blood Counts in Dogs: Maximizing Diagnostic Information.Top Companion Anim Med. 2018 Dec;33(4):141-146. doi: 10.1053/j.tcam.2018.06.001. Epub 2018 Jun 3. Top Companion Anim Med. 2018. PMID: 30502865 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical Sensors and Biosensors for Point-of-Care Testing of Pets: Opportunities for Individualized Diagnostics of Companion Animals.ACS Sens. 2025 May 23;10(5):3222-3238. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.4c03664. Epub 2025 Apr 22. ACS Sens. 2025. PMID: 40259889 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barroso T.G., Ribeiro L., Gregório H., Santos F., Martins R.C. Point-of-care Vis-SWNIR spectroscopy towards reagent-less hemogram analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021;343:130138. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2021.130138. - DOI
-
- Barroso T.G., Ribeiro L., Gregório H., Monteiro-Silva F., Neves dos Santos F., Martins R.C. Point-of-Care Using Vis-NIR Spectroscopy for White Blood Cell Count Analysis. Chemosensors. 2022;10:460. doi: 10.3390/chemosensors10110460. - DOI
-
- Olinger J.M., Griffiths P.R. Quantitative effects of an absorbing matrix on near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra. Anal. Chem. 1988;60:2427–2435. doi: 10.1021/ac00172a022. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

