Pars Interarticularis Fractures Treated with Minimally Invasive Surgery: A Literature Review
- PMID: 38276087
- PMCID: PMC10817087
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13020581
Pars Interarticularis Fractures Treated with Minimally Invasive Surgery: A Literature Review
Abstract
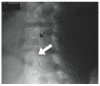
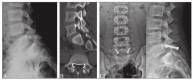
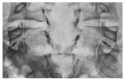
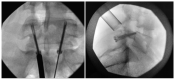
Recurrent stress on the isthmic pars interarticularis often leads to profound injury and symptom burden. When conservative and medical management fail, there are various operative interventions that can be used. The current review details the common clinical presentation and treatment of pars injury, with a special focus on the emerging minimally invasive procedures used in isthmic pars interarticularis repair. PubMed and Google Scholar database literature reviews were conducted. The keywords and phrases that were searched include but were not limited to; "history of spondylolysis", "pars interarticularis", "pars defect", "conventional surgical repair of pars", and "minimally invasive repair of pars". The natural history, conventional presentation, etiology, risk factors, and management of pars interarticularis injury are discussed by the authors. The surgical interventions described include the Buck's repair, Morscher Screw-Hook repair, Scott's Wiring technique, and additional pedicle screw-based repairs. Minimally invasive techniques are also reviewed, including the Levi technique. Surgical intervention has been proven to be safe and effective in managing pars interarticularis fractures. However, minimally invasive techniques often provide additional benefit to patients such as reducing damage of surrounding structures, decreasing postoperative pain, and limiting the time away from sports and other activities.
Keywords: minimally invasive; pars interarticularis; percutaneous pedicle screws.
Conflict of interest statement
Allan D. Levi receives teaching honorarium from the American Association of Neurological Surgeons and grant support from the Department of Defense and the National Institutes of Health (NIH-NINDS).
Figures






Similar articles
-
Repair of isthmic pars interarticularis fractures: a literature review of conventional and minimally invasive techniques.J Neurosurg Sci. 2019 Jun;63(3):318-329. doi: 10.23736/S0390-5616.19.04646-0. J Neurosurg Sci. 2019. PMID: 31096726 Review.
-
Does Direct Surgical Repair Benefit Pars Interarticularis Fracture? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Pain Physician. 2022 May;25(3):265-282. Pain Physician. 2022. PMID: 35652766
-
Repair of the pars interarticularis defect with a cable-screw construct. A preliminary report.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998 Jan 15;23(2):263-9. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199801150-00023. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998. PMID: 9474736
-
Spondylolysis outcomes in adolescents after direct screw repair of the pars interarticularis.J Neurosurg Spine. 2014 Sep;21(3):329-33. doi: 10.3171/2014.5.SPINE13772. Epub 2014 Jun 20. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014. PMID: 24949906
-
A comparison of the techniques of direct pars interarticularis repairs for spondylolysis and low-grade spondylolisthesis: a meta-analysis.Neurosurg Focus. 2018 Jan;44(1):E10. doi: 10.3171/2017.11.FOCUS17581. Neurosurg Focus. 2018. PMID: 29290131
Cited by
-
Impact of asymmetric L4-L5 facet joint degeneration on lumbar spine biomechanics using a finite element approach.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 12;15(1):12613. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97021-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40221590 Free PMC article.
-
Lumbar Spondylolysis: Future Perspectives.JMA J. 2024 Oct 15;7(4):541-542. doi: 10.31662/jmaj.2024-0202. Epub 2024 Sep 27. JMA J. 2024. PMID: 39513053 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Treatment of lumbar spondylolysis in young adults using modified intravertebral screw-rod fixation system for single vertebral body combined with autologous cancellous bone graft: a technical note and preliminary report.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Dec 23;19(1):868. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05382-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39710685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mansfield J.T., Wroten M. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2023. Pars Interarticularis Defect. - PubMed
-
- Kim H.S., Kashlan O.N., Singh R., Adsul N.M., Yong Z., Oh S.W., Noh J.H., Jang I.T., Oh S.H. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation of the Sinuvertebral Nerve in an Olympian with a Left L5 Pedicle/Pars Interarticularis Fracture-Associated Left L5-S1 Disk Desiccation. World Neurosurg. X. 2019;3:100032. doi: 10.1016/j.wnsx.2019.100032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mohammed N., Patra D.P., Narayan V., Savardekar A.R., Dossani R.H., Bollam P., Bir S., Nanda A. A comparison of the techniques of direct pars interarticularis repairs for spondylolysis and low-grade spondylolisthesis: A meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Focus. 2018;44:E10. doi: 10.3171/2017.11.FOCUS17581. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

