Utility of an In-Vitro Micro-Neutralizing Test in Comparison to a Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test for Dengue Virus, Japanese Encephalitis Virus, and Zika Virus Serology and Drug Screening
- PMID: 38276154
- PMCID: PMC10821437
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens13010008
Utility of an In-Vitro Micro-Neutralizing Test in Comparison to a Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test for Dengue Virus, Japanese Encephalitis Virus, and Zika Virus Serology and Drug Screening
Abstract
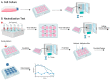
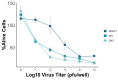
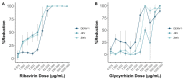
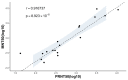
Flavivirus infections, including dengue virus (DENV), Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), and Zika virus (ZIKV), present significant global public health challenges. For successful vaccine design, the assessment of neutralizing antibody activity requires reliable and robust methodologies for determining antibody titers. Although the plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT) is commonly acknowledged as the gold standard, it has limitations in terms of time and cost, and its usage may be limited in resource-limited settings. To address these challenges, we introduced the micro-neutralization test (MNT) as a simplified alternative to the PRNT. The MNT employs a 96-well plate format, conducts microscale neutralization assays, and assesses cell viability by dissolving cells to create a uniform color solution, which is measured with a spectrometer. In this study, we evaluated the utility of the MNT by contrasting the end-point titers of the MNT and PRNT using 4 monoclonal antibodies, 15 non-human primate serum samples, and 2 therapeutic drug candidates across flaviviruses. The results demonstrated a strong correlation between the MNT and PRNT titers, affirming the robustness and reproducibility of the MNT for evaluating control measures against flaviviruses. This research contributes valuable insights toward the development of a cost-effective antibody titer testing approach that is particularly suitable for resource-limited settings.
Keywords: Japanese encephalitis virus; Zika; dengue; flavivirus; microneutralization test; neutralizing antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Incorporation of IgG Depletion in a Neutralization Assay Facilitates Differential Diagnosis of Zika and Dengue in Secondary Flavivirus Infection Cases.J Clin Microbiol. 2018 May 25;56(6):e00234-18. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00234-18. Print 2018 Jun. J Clin Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29618505 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of Flavivirus Neutralizing Antibodies in Thailand by High-Throughput Neutralization Assay: Endemic Circulation of Zika Virus before 2012.mSphere. 2021 Aug 25;6(4):e0033921. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00339-21. Epub 2021 Jul 14. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34259560 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of cross-reactivity between flaviviruses with sera of patients with Japanese encephalitis showed the importance of neutralization tests for the diagnosis of Japanese encephalitis.J Infect Chemother. 2019 Oct;25(10):786-790. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 May 16. J Infect Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31105002
-
Modulation of Dengue/Zika Virus Pathogenicity by Antibody-Dependent Enhancement and Strategies to Protect Against Enhancement in Zika Virus Infection.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 23;9:597. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00597. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29740424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-reactive dengue virus-derived monoclonal antibodies to Zika virus envelope protein: Panacea or Pandora's box?BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Dec 10;18(1):641. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3572-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30526531 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of flavivirus RNA stability and infectivity in various water environments.Trop Med Health. 2025 Jan 24;53(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s41182-025-00686-9. Trop Med Health. 2025. PMID: 39856772 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of systemic and mucosal immune response against Zika virus by vaccination with non-infectious chimeric VLPs.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 10;15(1):24834. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07059-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40640219 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Conditions for Expression of Dengue Serotype 2 EDIII Protein in Escherichia coli and Immune Responses of Adjuvant-Free EDIII Ferritin Nanoparticles Against Dengue Virus in BALB/c Mice.Viruses. 2025 Jan 17;17(1):129. doi: 10.3390/v17010129. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 39861918 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

