Stretch Sensor: Development of Biodegradable Film
- PMID: 38276377
- PMCID: PMC10821183
- DOI: 10.3390/s24020683
Stretch Sensor: Development of Biodegradable Film
Abstract
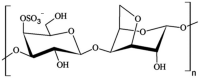
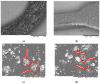
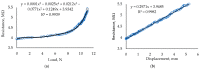
This article presents research on biodegradable stretch sensors produced using biological material. This sensor uses a piezoresistive effect to indicate stretch, which can be used for force measurement. In this work, an attempt was made to develop the composition of a sensitive material and to design a sensor. The biodegradable base was made from a κ-carrageenan compound mixed with Fe2O3 microparticles and glycerol. The influence of the weight fraction and iron oxide microparticles on the tensile strength and Young's modulus was experimentally investigated. Tensile test specimens consisted of 10-25% iron oxide microparticles of various sizes. The results showed that increasing the mass fraction of the reinforcement improved the Young's modulus compared to the pure sample and decreased the elongation percentage. The GF of the developed films varies from 0.67 to 10.47 depending on composition. In this paper, it was shown that the incorporation of appropriate amounts of Fe2O3 microparticles into κ-carrageenan can achieve dramatic improvements in mechanical properties, resulting in elongation of up to 10%. The developed sensors were experimentally tested, and their sensitivity, stability, and range were determined. Finally, conclusions were drawn on the results obtained.
Keywords: biodegradable; force sensor; iron (III) oxide; stretch sensor; κ-carrageenan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



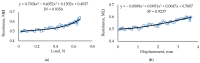

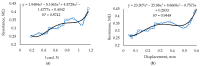
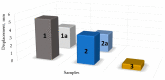
Similar articles
-
Biodegradable Carrageenan-Based Force Sensor: An Experimental Approach.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 26;23(23):9423. doi: 10.3390/s23239423. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067796 Free PMC article.
-
Toward predicting tensile strength of pharmaceutical tablets by ultrasound measurement in continuous manufacturing.Int J Pharm. 2016 Jun 30;507(1-2):83-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.04.064. Epub 2016 May 5. Int J Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27157310
-
Modeling and analysis of film composition on mechanical properties of maize starch based edible films.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013 Nov;62:565-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.09.027. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013. PMID: 24080451
-
Physicochemical characterization of kappa-carrageenan (Euchema cottoni) based films incorporated with various plant oils.Carbohydr Polym. 2017 Feb 10;157:1479-1487. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.11.026. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Carbohydr Polym. 2017. PMID: 27987859
-
Biodegradable κ-carrageenan/nanoclay nanocomposite films containing Rosmarinus officinalis L. extract for improved strength and antibacterial performance.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Aug;115:227-235. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.051. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29660461
References
-
- Cai H., Zhang D., Zhang H., Tang M., Xu Z., Xia H., Li K., Wang J. Trehalose-enhanced ionic conductive hydrogels with extreme stretchability, self-adhesive and anti-freezing abilities for both flexible strain sensor and all-solid-state supercapacitor. Chem. Eng. J. 2023;472:144849. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.144849. - DOI
-
- Sandford P.A., Baird J. The Polysaccharides. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 1983. Industrial Utilization of Polysaccharides; pp. 411–490. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

