IIoT Low-Cost ZigBee-Based WSN Implementation for Enhanced Production Efficiency in a Solar Protection Curtains Manufacturing Workshop
- PMID: 38276403
- PMCID: PMC10818594
- DOI: 10.3390/s24020712
IIoT Low-Cost ZigBee-Based WSN Implementation for Enhanced Production Efficiency in a Solar Protection Curtains Manufacturing Workshop
Abstract
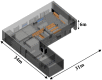
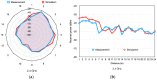
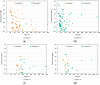
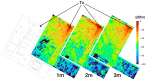
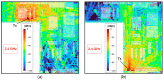
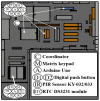
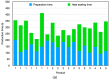
Nowadays, the Industry 4.0 concept and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) are considered essential for the implementation of automated manufacturing processes across various industrial settings. In this regard, wireless sensor networks (WSN) are crucial due to their inherent mobility, easy deployment and maintenance, scalability, and low power consumption, among other benefits. In this context, the presented paper proposes an optimized and low-cost WSN based on ZigBee communication technology for the monitoring of a real manufacturing facility. The company designs and manufactures solar protection curtains and aims to integrate the deployed WSN into the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system in order to optimize their production processes and enhance production efficiency and cost estimation capabilities. To achieve this, radio propagation measurements and 3D ray launching simulations were conducted to characterize the wireless channel behavior and facilitate the development of an optimized WSN system that can operate in the complex industrial environment presented and validated through on-site wireless channel measurements, as well as interference analysis. Then, a low-cost WSN was implemented and deployed to acquire real-time data from different machinery and workstations, which will be integrated into the ERP system. Multiple data streams have been collected and processed from the shop floor of the factory by means of the prototype wireless nodes implemented. This integration will enable the company to optimize its production processes, fabricate products more efficiently, and enhance its cost estimation capabilities. Moreover, the proposed system provides a scalable platform, enabling the integration of new sensors as well as information processing capabilities.
Keywords: 3D ray launching; Industry 4.0; automation; industrial internet of things; manufacturing process; wireless channel; wireless sensor networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures










References
-
- Sisinni E., Saifullah A., Han S., Jennehag U., Gidlund M. Industrial Internet of Things: Challenges, Opportunities, and Directions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018;14:4724–4734. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2852491. - DOI
-
- Ahmed A., Valtiner D., Thomos C., Dielacher F. Wireless connectivity in Industrial sensor and control networks: Challenges and issues in a real implementation for a smart production use-case; Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA); Vienna, Austria. 8–11 September 2020.
-
- Islam K., Shen W., Wang X. Wireless Sensor Network Reliability and Security in Factory Automation: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2012;42:1243–1256. doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2012.2205680. - DOI
-
- Song Y., Yu F.R., Zhou L., Yang X., He Z. Applications of the Internet of Things (IoT) in Smart Logistics: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021;8:4250–4274. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3034385. - DOI
-
- Lu X., Kim I.H., Xhafa A., Zhou J. WSN for Machine Area Network applications; Proceedings of the 46th European Solid-State Device Research Conference (ESSDERC); Lausanne, Switzerland. 12–15 September 2016.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

