New Trends to Treat Muscular Atrophy: A Systematic Review of Epicatechin
- PMID: 38276564
- PMCID: PMC10818576
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16020326
New Trends to Treat Muscular Atrophy: A Systematic Review of Epicatechin
Abstract
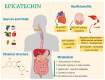
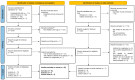
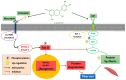
Epicatechin is a polyphenol compound that promotes skeletal muscle differentiation and counteracts the pathways that participate in the degradation of proteins. Several studies present contradictory results of treatment protocols and therapeutic effects. Therefore, the objective of this systematic review was to investigate the current literature showing the molecular mechanism and clinical protocol of epicatechin in muscle atrophy in humans, animals, and myoblast cell-line. The search was conducted in Embase, PubMed/MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science. The qualitative analysis demonstrated that there is a commonness of epicatechin inhibitory action in myostatin expression and atrogenes MAFbx, FOXO, and MuRF1. Epicatechin showed positive effects on follistatin and on the stimulation of factors related to the myogenic actions (MyoD, Myf5, and myogenin). Furthermore, the literature also showed that epicatechin can interfere with mitochondrias' biosynthesis in muscle fibers, stimulation of the signaling pathways of AKT/mTOR protein production, and amelioration of skeletal musculature performance, particularly when combined with physical exercise. Epicatechin can, for these reasons, exhibit clinical applicability due to the beneficial results under conditions that negatively affect the skeletal musculature. However, there is no protocol standardization or enough clinical evidence to draw more specific conclusions on its therapeutic implementation.
Keywords: catechins; epicatechin; muscular atrophy; myogenic regulatory factors; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Furthermore, the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucosamine inhibits myoblast proliferation and differentiation, and stimulates myotube atrophy through distinct signal pathways.J Nutr Biochem. 2025 Jan;135:109762. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109762. Epub 2024 Sep 7. J Nutr Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39251145
-
Multi-therapeutic strategy targeting Akt-mTOR and FoxO1 pathway to counteract skeletal muscle atrophy consecutive to hypoxia.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025 Jun 1;328(6):C2057-C2069. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00851.2024. Epub 2025 May 6. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40327324
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
-
Umbelliferone attenuates diabetic sarcopenia by modulating mitochondrial quality and the ubiquitin-proteasome system.Phytomedicine. 2025 Aug;144:156930. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156930. Epub 2025 May 31. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40483791
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
Cited by
-
Phytochemicals act holistically to enhance host defenses during poultry coccidiosis.Poult Sci. 2025 May;104(5):105042. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105042. Epub 2025 Mar 15. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40120241 Free PMC article.
-
Epicatechin Decreases UCP2 Gene Expression in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells by the Presence of a Regulatory Element in the Promoter.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 25;26(9):4102. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094102. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362341 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Impact of Catechins on Bone Metabolism: A Comprehensive Review of Current Research and Future Directions.Metabolites. 2024 Oct 18;14(10):560. doi: 10.3390/metabo14100560. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39452941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of Phenolic Profiles and Antioxidant Activity in the Leaves of Invasive Amelanchier × spicata (Lam.) K. Koch in Lithuania.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jan 14;14(2):221. doi: 10.3390/plants14020221. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861574 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Impairment, Muscle Atrophy, and Cognitive Decline: Critical Age-Related Conditions.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 13;12(9):2096. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092096. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Araújo C.R.R., de Melo Silva T., Dos Santos M.G., Ottoni M.H.F., de Souza Fagundes E.M., de Sousa Fontoura H., de Melo G.E.B.A., de Carvalho Alcântara A.F. Anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activities of the extracts, fractions, and chemical constituents isolated from luehea ochrophylla mart. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019;19:284. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2701-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

