Molecular Characterization of the Recombinant Ig1 Axl Receptor Domain: An Intriguing Bait for Screening in Drug Discovery
- PMID: 38276597
- PMCID: PMC10818745
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29020521
Molecular Characterization of the Recombinant Ig1 Axl Receptor Domain: An Intriguing Bait for Screening in Drug Discovery
Abstract
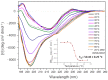
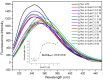
Axl receptor tyrosine kinase and its ligand Gas6 regulate several biological processes and are involved in both the onset and progression of tumor malignancies and autoimmune diseases. Based on its key role in these settings, Axl is considered a promising target for the development of molecules with therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. In this paper, we describe the molecular characterization of the recombinant Ig1 domain of Axl (Ig1 Axl) and its biochemical properties. For the first time, an exhaustive spectroscopic characterization of the recombinant protein through circular dichroism and fluorescence studies is also reported, as well as a binding analysis to its natural ligand Gas6, paving the way for the use of recombinant Ig1 Axl as a bait in drug discovery screening procedures aimed at the identification of novel and specific binders targeting the Axl receptor.
Keywords: Axl receptor; circular dichroism; drug discovery; fluorescence spectroscopy; iodoacetamide; protein refolding; recombinant Ig1 domain; trypsin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tsou W.I., Nguyen K.Q., Calarese D.A., Garforth S.J., Antes A.L., Smirnov S.V., Almo S.C., Birge R.B., Kotenko S.V. Receptor tyrosine kinases, TYRO3, AXL, and MER, demonstrate distinct patterns and complex regulation of ligand-induced activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014;289:25750–25763. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.569020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meertens L., Labeau A., Dejarnac O., Cipriani S., Sinigaglia L., Bonnet-Madin L., Le Charpentier T., Hafirassou M.L., Zamborlini A., Cao-Lormeau V.M., et al. Axl Mediates ZIKA Virus Entry in Human Glial Cells and Modulates Innate Immune Responses. Cell Rep. 2017;18:324–333. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.045. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

