Testing the Feasibility and Acceptability of Using an Artificial Intelligence Chatbot to Promote HIV Testing and Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis in Malaysia: Mixed Methods Study
- PMID: 38277206
- PMCID: PMC10858413
- DOI: 10.2196/52055
Testing the Feasibility and Acceptability of Using an Artificial Intelligence Chatbot to Promote HIV Testing and Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis in Malaysia: Mixed Methods Study
Abstract
Background: The HIV epidemic continues to grow fastest among men who have sex with men (MSM) in Malaysia in the presence of stigma and discrimination. Engaging MSM on the internet using chatbots supported through artificial intelligence (AI) can potentially help HIV prevention efforts. We previously identified the benefits, limitations, and preferred features of HIV prevention AI chatbots and developed an AI chatbot prototype that is now tested for feasibility and acceptability.
Objective: This study aims to test the feasibility and acceptability of an AI chatbot in promoting the uptake of HIV testing and pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in MSM.
Methods: We conducted beta testing with 14 MSM from February to April 2022 using Zoom (Zoom Video Communications, Inc). Beta testing involved 3 steps: a 45-minute human-chatbot interaction using the think-aloud method, a 35-minute semistructured interview, and a 10-minute web-based survey. The first 2 steps were recorded, transcribed verbatim, and analyzed using the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology. Emerging themes from the qualitative data were mapped on the 4 domains of the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology: performance expectancy, effort expectancy, facilitating conditions, and social influence.
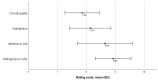
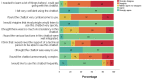
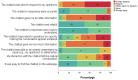
Results: Most participants (13/14, 93%) perceived the chatbot to be useful because it provided comprehensive information on HIV testing and PrEP (performance expectancy). All participants indicated that the chatbot was easy to use because of its simple, straightforward design and quick, friendly responses (effort expectancy). Moreover, 93% (13/14) of the participants rated the overall chatbot quality as high, and all participants perceived the chatbot as a helpful tool and would refer it to others. Approximately 79% (11/14) of the participants agreed they would continue using the chatbot. They suggested adding a local language (ie, Bahasa Malaysia) to customize the chatbot to the Malaysian context (facilitating condition) and suggested that the chatbot should also incorporate more information on mental health, HIV risk assessment, and consequences of HIV. In terms of social influence, all participants perceived the chatbot as helpful in avoiding stigma-inducing interactions and thus could increase the frequency of HIV testing and PrEP uptake among MSM.
Conclusions: The current AI chatbot is feasible and acceptable to promote the uptake of HIV testing and PrEP. To ensure the successful implementation and dissemination of AI chatbots in Malaysia, they should be customized to communicate in Bahasa Malaysia and upgraded to provide other HIV-related information to improve usability, such as mental health support, risk assessment for sexually transmitted infections, AIDS treatment, and the consequences of contracting HIV.
Keywords: HIV prevention; HIV testing; MSM; PrEP; acceptability; artificial intelligence; chatbot; feasibility; mHealth; men who have sex with men; mobile health; mobile phone; preexposure prophylaxis.
©Min Hui Cheah, Yan Nee Gan, Frederick L Altice, Jeffrey A Wickersham, Roman Shrestha, Nur Afiqah Mohd Salleh, Kee Seong Ng, Iskandar Azwa, Vimala Balakrishnan, Adeeba Kamarulzaman, Zhao Ni. Originally published in JMIR Human Factors (https://humanfactors.jmir.org), 26.01.2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Formative Evaluation of the Acceptance of HIV Prevention Artificial Intelligence Chatbots By Men Who Have Sex With Men in Malaysia: Focus Group Study.JMIR Form Res. 2022 Oct 6;6(10):e42055. doi: 10.2196/42055. JMIR Form Res. 2022. PMID: 36201390 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Usability of an HIV Prevention Artificial Intelligence Chatbot in Malaysia: National Observational Study.JMIR Hum Factors. 2025 Jul 15;12:e70034. doi: 10.2196/70034. JMIR Hum Factors. 2025. PMID: 40663792 Free PMC article.
-
Clinic-Integrated Smartphone App (JomPrEP) to Improve Uptake of HIV Testing and Pre-exposure Prophylaxis Among Men Who Have Sex With Men in Malaysia: Mixed Methods Evaluation of Usability and Acceptability.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2023 Feb 16;11:e44468. doi: 10.2196/44468. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2023. PMID: 36795465 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Demand creation and retention strategies for oral pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention among men who have sex with men and transgender women: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 14;23(1):793. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08693-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37964202 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Generative Conversational Artificial Intelligence on the Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Queer Community: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Dec 6;25:e52091. doi: 10.2196/52091. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37864350 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of human immunodeficiency virus-related risky sexual behaviors between men who have sex with men only and men who have sex with men and women: A cross-sectional study in Eastern China.Prev Med Rep. 2024 Oct 30;48:102923. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2024.102923. eCollection 2024 Dec. Prev Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39555239 Free PMC article.
-
Formative evaluation of the acceptance of HIV prevention Artificial Intelligence chatbots by Black gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men in the Southern United States: Focus group study.PLOS Digit Health. 2025 Jun 4;4(6):e0000891. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000891. eCollection 2025 Jun. PLOS Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40465591 Free PMC article.
-
Preferences for eHealth interventions to improve sexual health and prevent HIV for Vietnamese young men who have sex with men.Health Promot Int. 2025 May 13;40(3):daaf060. doi: 10.1093/heapro/daaf060. Health Promot Int. 2025. PMID: 40402019
-
User Input in the Development of Digital Sexual Health Tools: A Scoping Review and Guidance for Tool Developers.Health Expect. 2025 Aug;28(4):e70360. doi: 10.1111/hex.70360. Health Expect. 2025. PMID: 40717609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Perspective on Home-Based Sexual Health Care: Evidence, Access, and Future Directions.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2025 Feb 26;22(1):20. doi: 10.1007/s11904-025-00724-5. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2025. PMID: 40000537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- HIV and AIDS. World Health Organization. 2022. [2023-12-26]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids .
-
- New HIV infections increasingly among key populations. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/Aids. 2020. [2023-12-26]. https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/presscentre/featurestories/2020/sept... .
-
- Seizing the moment: tackling entrenched inequalities to end epidemics. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/Aids. 2020. http://tinyurl.com/4zyedprp .
-
- Suleiman A, Tze CP. Country progress report on HIV/AIDS 2019 Malaysia. HIV/STI/Hepatitis, C Section of Ministry of Health, Malaysia. 2019. [2023-12-22]. https://www.moh.gov.my/moh/resources/Penerbitan/Laporan/Umum/Report_GAM_... .
-
- Global AIDS monitoring: country progress report-Malaysia. Ministry of Health, Malaysia. 2021. [2023-12-26]. https://www.moh.gov.my/moh/resources/Penerbitan/Laporan/Umum/MYS_country... .
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous