Ketonuria in an adult with Prader-Willi syndrome and diabetes mellitus: A case report
- PMID: 38277514
- PMCID: PMC10817086
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037096
Ketonuria in an adult with Prader-Willi syndrome and diabetes mellitus: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) is a genetic disorder affecting multiple systems. Approximately one-quarter of PWS patients will develop diabetes. Given the uncontrolled hyperphagia and resultant severe obesity in these patients, their glycemic management poses a significant challenge.
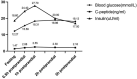
Case report: We present the clinical profile of a male patient diagnosed with both PWS and diabetes. Previous administration of the sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor Canagliflozin resulted in improved glycemic control and weight management. But at the age of 25, the patient was hospitalized due to worsened glycemic control and the detection of ketonuria. After thorough examination and clinical observation, we discovered that the patient ketonuria was associated with enhanced lipid metabolism related to Canagliflozin. After excluding the risk of SGLT-2 inhibitor-induced euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis, adjustments of the hypoglycemic regimen, building upon prior treatment, were recommended for the patient.
Conclusion: It is important to note that among patients with both PWS and diabetes, the utilization of SGLT-2 inhibitors can lead to the emergence of ketonuria due to increased lipolysis. Therefore, any decision to discontinue SGLT-2 inhibitors should undergo thorough evaluation.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improvement in glycaemic parameters using SGLT-2 inhibitor and GLP-1 agonist in combination in an adolescent with diabetes mellitus and Prader-Willi syndrome: a case report.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jul 28;33(7):951-955. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2019-0389. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32447330
-
Fournier's Gangrene and Diabetic Ketoacidosis Associated with Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors: Life-Threatening Complications.Am J Case Rep. 2020 Jun 2;21:e921536. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.921536. Am J Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32483108 Free PMC article.
-
[Diabetic euglycemic ketosis or ketoacidosis in individuals with type 2 diabetes treated by SGLT2 inhibitors: A series of Belgian clinical cases].Rev Med Interne. 2020 Apr;41(4):226-231. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2019.12.006. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Rev Med Interne. 2020. PMID: 31866073 French.
-
Severe euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis of multifactorial etiology in a type 2 diabetic patient treated with empagliflozin: case report and literature review.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Jul 15;21(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-01930-6. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32669085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of semaglutide on weight loss and glycaemic control in patients with Prader-Willi Syndrome and type 2 diabetes.Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2024 Feb;71(2):83-87. doi: 10.1016/j.endien.2023.12.001. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2024. PMID: 38553173 Review.
References
-
- Cassidy SB, Schwartz S, Miller JL, et al. . Prader-Willi syndrome. Genet Med. 2012;14:10–26. - PubMed
-
- Butler JV, Whittington JE, Holland AJ, et al. . Prevalence of, and risk factors for, physical ill-health in people with Prader-Willi syndrome: a population-based study. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2002;44:248–55. - PubMed
-
- Vogels A, Fryns JP. Age at diagnosis, body mass index and physical morbidity in children and adults with the Prader-Willi syndrome. Genet Couns. 2004;15:397–404. - PubMed
-
- Sinnema M, Maaskant MA, van Schrojenstein Lantman-de Valk HM, et al. . Physical health problems in adults with Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155:2112–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical