The Role of CD4/6 Inhibitors in Breast Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 38279242
- PMCID: PMC10816395
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25021242
The Role of CD4/6 Inhibitors in Breast Cancer Treatment
Abstract
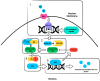
Over the last decade, treatment paradigms for breast cancer have undergone a renaissance, particularly in hormone-receptor-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer. These revolutionary therapies are based on the selective targeting of aberrancies within the cell cycle. This shift towards targeted therapies has also changed the landscape of disease monitoring. In this article, we will review the fundamentals of cell cycle progression in the context of the new cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. In addition to discussing the currently approved cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors for breast cancer, we will explore the ongoing development and search for predictive biomarkers and modalities to monitor treatment.
Keywords: CDK inhibitors; ER+/HER2− breast cancer; ctDNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors L.P., C.J., T.G., A.C. and A.H. were employed by the company Memorial Health System. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- U.S. Cancer Statistics Data Visualizations Tool|CDC. [(accessed on 1 September 2023)];2023 June 9; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/uscs/dataviz/index.htm.
-
- Finn R.S., Boer K., Bondarenko I., Patel R., Pinter T., Schmidt M., Shparyk Y.V., Thummala A., Voitko N., Bananis E., et al. Overall Survival Results from the Randomized Phase 2 Study of Palbociclib in Combination with Letrozole versus Letrozole Alone for First-Line Treatment of ER+/HER2− Advanced Breast Cancer (PALOMA-1, TRIO-18) Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020;183:419–428. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05755-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rugo H.S., Finn R.S., Diéras V., Ettl J., Lipatov O., Joy A.A., Harbeck N., Castrellon A., Iyer S., Lu D.R., et al. Palbociclib plus Letrozole as First-Line Therapy in Estrogen Receptor-Positive/Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer with Extended Follow-Up. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019;174:719–729. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-05125-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cristofanilli M., Turner N.C., Bondarenko I., Ro J., Im S.A., Masuda N., Colleoni M., DeMichele A., Loi S., Verma S., et al. Fulvestrant plus Palbociclib versus Fulvestrant plus Placebo for Treatment of Hormone-Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer That Progressed on Previous Endocrine Therapy (PALOMA-3): Final Analysis of the Multicentre, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:425–439. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00613-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

