A natural substitution of a conserved amino acid in eIF4E confers resistance against multiple potyviruses
- PMID: 38279849
- PMCID: PMC10777747
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.13418
A natural substitution of a conserved amino acid in eIF4E confers resistance against multiple potyviruses
Abstract
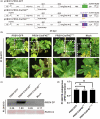
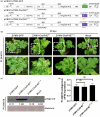
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E), which plays a pivotal role in initiating translation in eukaryotic organisms, is often hijacked by the viral genome-linked protein to facilitate the infection of potyviruses. In this study, we found that the naturally occurring amino acid substitution D71G in eIF4E is widely present in potyvirus-resistant watermelon accessions and disrupts the interaction between watermelon eIF4E and viral genome-linked protein of papaya ringspot virus-watermelon strain, zucchini yellow mosaic virus or watermelon mosaic virus. Multiple sequence alignment and protein modelling showed that the amino acid residue D71 located in the cap-binding pocket of eIF4E is strictly conserved in many plant species. The mutation D71G in watermelon eIF4E conferred resistance against papaya ringspot virus-watermelon strain and zucchini yellow mosaic virus, and the equivalent mutation D55G in tobacco eIF4E conferred resistance to potato virus Y. Therefore, our finding provides a potential precise target for breeding plants resistant to multiple potyviruses.
Keywords: Potyvirus; PRSV-W; PVY; ZYMV; eIF4E; recessive resistance.
© 2024 The Authors. Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Naturally Occurring Amino Acid Substitution in the VPg α1-α2 Loop Breaks eIF4E-Mediated Resistance to PRSV by Enabling VPg to Re-Hijack Another eIF4E Isoform eIF(iso)4E in Watermelon.Mol Plant Pathol. 2024 Nov;25(11):e70033. doi: 10.1111/mpp.70033. Mol Plant Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39587435 Free PMC article.
-
Non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in the watermelon eIF4E gene are closely associated with resistance to zucchini yellow mosaic virus.Theor Appl Genet. 2009 Dec;120(1):191-200. doi: 10.1007/s00122-009-1169-0. Epub 2009 Oct 10. Theor Appl Genet. 2009. PMID: 19820912
-
A natural recessive resistance gene against potato virus Y in pepper corresponds to the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E).Plant J. 2002 Dec;32(6):1067-75. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01499.x. Plant J. 2002. PMID: 12492847
-
Helper component proteinase of the genus Potyvirus is an interaction partner of translation initiation factors eIF(iso)4E and eIF4E and contains a 4E binding motif.J Virol. 2011 Jul;85(13):6784-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00485-11. Epub 2011 Apr 27. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21525344 Free PMC article.
-
Natural variation and functional analyses provide evidence for co-evolution between plant eIF4E and potyviral VPg.Plant J. 2008 Apr;54(1):56-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03407.x. Epub 2008 Jan 7. Plant J. 2008. PMID: 18182024
Cited by
-
Fine mapping of the Chilli veinal mottle virus resistance 4 (cvr4) gene in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2025 Jan 7;138(1):19. doi: 10.1007/s00122-024-04805-8. Theor Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 39777543 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Cowpea Resistance to Potyvirus: Assessment of eIF4E Gene Mutations and Their Impact on the eIF4E-VPg Protein Interaction.Viruses. 2025 Jul 28;17(8):1050. doi: 10.3390/v17081050. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40872765 Free PMC article.
-
Oligomeric SWEET1g of Solanum tuberosum confers resistance to potato virus Y and Potato virus X.Plant J. 2025 Aug;123(3):e70400. doi: 10.1111/tpj.70400. Plant J. 2025. PMID: 40758984 Free PMC article.
-
Viral tropism in plants, reproductive tissues, and seeds.Arch Microbiol. 2025 May 23;207(7):152. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04353-9. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40404962 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agaoua, A. , Rittener, V. , Troadec, C. , Desbiez, C. , Bendahmane, A. , Moquet, F. et al. (2022) A single substitution in vacuolar protein sorting 4 is responsible for resistance to watermelon mosaic virus in melon. Journal of Experimental Botany, 73, 4008–4021. - PubMed
-
- Amano, M. , Mochizuki, A. , Kawagoe, Y. , Iwahori, K. , Niwa, K. , Svoboda, J. et al. (2013) High‐resolution mapping of zym, a recessive gene for zucchini yellow mosaic virus resistance in cucumber. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 126, 2983–2993. - PubMed
-
- Andrade, M. , Abe, Y. , Nakahara, K.S. & Uyeda, I. (2009) The cyv‐2 resistance to clover yellow vein virus in pea is controlled by the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 75, 241–249.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

