Modified medication use in dysphagia: the effect of thickener on drug bioavailability-a systematic review
- PMID: 38280090
- PMCID: PMC10876765
- DOI: 10.1007/s41999-023-00896-6
Modified medication use in dysphagia: the effect of thickener on drug bioavailability-a systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Dysphagia is associated with long-term conditions including strokes, dementia, Parkinson's disease and frailty. Dysphagia affects 30-40% of the population aged over 65 years-old. Adults with dysphagia often experience long-term conditions requiring multiple medications (often > 5) to manage these. The thickening of liquids is a common compensatory strategy in dysphagia management. Studies suggest that immersion in thickened liquids affects medicines' solubility in vitro. Clinicians and pharmacists are unaware of the pharmacokinetic/therapeutic effects of thickened liquids on oral medicines. We conducted a systematic review of existing literature on thickeners' effects on drug bioavailability.
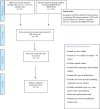
Methodology: We performed a literature search of MEDLINE & EMBASE. Search terms included: dysphagia/thickened diet (EMBASE only)/ bioavailability or absorption of medicines or pharmacokinetics; excluded: NG feeds/animal studies.
Studies included: all genders, countries, > 18 years, community and hospital settings. PRISMA guidance was followed.
Results: Five hundred seventy results were found, and 23 articles identified following the reference list review. Following an abstract and full-text review, 18 were included. Most articles evaluated thickeners on dissolution profiles in-vitro, with a few investigating in-vivo. Most studies were single-centre prospective studies identifying that thickeners generally affect dissolution rates of medications. Few studies assessed bioavailability or used clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: Dysphagia and polypharmacy are common in older adults, but little is known about the effects of altering liquid viscosity on the therapeutic effect of most medications. Further larger-scale studies are required to evaluate the therapeutic impact of thickener, on a bigger range of medications, factoring in other variables such as type of thickener, viscosity of thickener and duration of immersion.
Keywords: Bioavailability; Dysphagia; Modified diets; Swallowing; Thickened-liquids; Thickener.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no direct or indirect financial or non-financial interests relating to the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Do Thickening Agents Used in Dysphagia Diet Affect Drug Bioavailability?Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022 Jul 1;174:106197. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106197. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35489612
-
Sensory and rheological characteristics of thickened liquids differing concentrations of a xanthan gum-based thickener.J Texture Stud. 2017 Dec;48(6):571-585. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12268. Epub 2017 May 25. J Texture Stud. 2017. PMID: 28419504
-
Effect of thickener on disintegration, dissolution and permeability of common drug products for elderly patients.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020 Aug;153:168-176. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.06.005. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020. PMID: 32561342
-
Effect of Bolus Viscosity on the Safety and Efficacy of Swallowing and the Kinematics of the Swallow Response in Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: White Paper by the European Society for Swallowing Disorders (ESSD).Dysphagia. 2016 Apr;31(2):232-49. doi: 10.1007/s00455-016-9696-8. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Dysphagia. 2016. PMID: 27016216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thickening agents used for dysphagia management: effect on bioavailability of water, medication and feelings of satiety.Nutr J. 2013 May 1;12:54. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-12-54. Nutr J. 2013. PMID: 23634758 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Food Physical Properties on Oral Drug Absorption: A Comprehensive Review.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jan 16;19:267-280. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S497515. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39834644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Thickened Water on Ciprofloxacin Pharmacokinetics: A Comparative Study in Adult Males.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 5;13(15):4573. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154573. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124837 Free PMC article.
-
Solid Medication Intake in Hospitalised Patients With Dysphagia: A Challenge for Speech and Language Pathologists?Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025 Jul-Aug;60(4):e70073. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.70073. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025. PMID: 40605450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petchey L, Gentry T (2019) More harm than good—why more isn’t always better with older people’s medicines. Age UK
-
- Clave P, Rofes L, Carrion S, Ortegra O, Cabre M, Serra-Prat M, Arreola V (2012) Pathophysiology, relevance and natural history of oropharyngeal dysphagia among older people. pp 57-66. 10.1159/000339986 (Nestle Nutrition Institute workshop series) - PubMed
-
- Mateos-Nozal J, Sánchez García E, Montero-Errasquín B, Romero Rodríguez E, Cruz-Jentoft AJ. Short-term therapeutic adherence of hospitalized older patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia after an education intervention: analysis of compliance rates, risk factors and associated complications. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):413. doi: 10.3390/nu14030413. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical