Sexual dimorphism in melanocyte stem cell behavior reveals combinational therapeutic strategies for cutaneous repigmentation
- PMID: 38280858
- PMCID: PMC10821900
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45034-3
Sexual dimorphism in melanocyte stem cell behavior reveals combinational therapeutic strategies for cutaneous repigmentation
Abstract
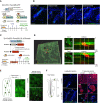
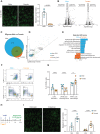
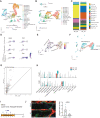
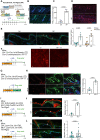
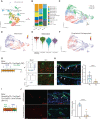
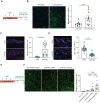
Vitiligo is an autoimmune skin disease caused by cutaneous melanocyte loss. Although phototherapy and T cell suppression therapy have been widely used to induce epidermal re-pigmentation, full pigmentation recovery is rarely achieved due to our poor understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms governing this process. Here, we identify unique melanocyte stem cell (McSC) epidermal migration rates between male and female mice, which is due to sexually dimorphic cutaneous inflammatory responses generated by ultra-violet B exposure. Using genetically engineered mouse models, and unbiased bulk and single-cell mRNA sequencing approaches, we determine that manipulating the inflammatory response through cyclooxygenase and its downstream prostaglandin product regulates McSC proliferation and epidermal migration in response to UVB exposure. Furthermore, we demonstrate that a combinational therapy that manipulates both macrophages and T cells (or innate and adaptive immunity) significantly promotes epidermal melanocyte re-population. With these findings, we propose a novel therapeutic strategy for repigmentation in patients with depigmentation conditions such as vitiligo.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
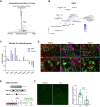
The corresponding author declares the following competing interests: Patent applicant: Cornell University. Name of the inventor: Andrew White. Application number: 63/496,967. Status of application: Pending. Specific aspect of manuscript covered in patent application: Figure 7, use of pge2 analog with uvb and uvb+ruxolitinib. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
Sexual dimorphism in melanocyte stem cell behavior reveals combinational therapeutic strategies for cutaneous repigmentation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 22:2023.05.22.541644. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.22.541644. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 27;15(1):796. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45034-3. PMID: 37293072 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

