MDM4 was associated with poor prognosis and tumor-immune infiltration of cancers
- PMID: 38281029
- PMCID: PMC10821240
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-024-01684-z
MDM4 was associated with poor prognosis and tumor-immune infiltration of cancers
Abstract
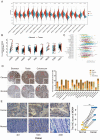
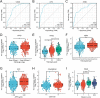
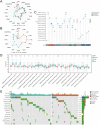
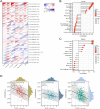
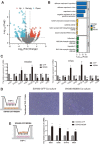
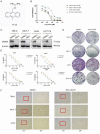
MDM4 is one of the MDM protein family and is generally recognized as the key negative regulator of p53. As a cancer-promoting factor, it plays a non-negligible role in tumorigenesis and development. In this article, we analyzed the expression levels of MDM4 in pan-cancer through multiple databases. We also investigated the correlations between MDM4 expression and prognostic value, immune features, genetic mutation, and tumor-related pathways. We found that MDM4 overexpression is often accompanied by adverse clinical features, poor prognosis, oncogenic mutations, tumor-immune infiltration and aberrant activation of oncogenic signaling pathways. We also conducted transcriptomic sequencing to investigate the effect of MDM4 on transcript levels in colon cancer and performed qPCR to verify this. Finally, we carried out some in vitro experiments including colony formation assay, chemoresistance and senescence-associated β-galactosidase activity assay to study the anti-tumor treatment effect of small molecule MDM4 inhibitor, NSC146109. Our research confirmed that MDM4 is a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target for a variety of malignancies.
Keywords: Inhibitor; MDM4; Pan-cancer; Prognostic biomarker; Tumor-immune infiltration.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MDM4 is a rational target for treating breast cancers with mutant p53.J Pathol. 2017 Apr;241(5):661-670. doi: 10.1002/path.4877. Epub 2017 Mar 1. J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28097652
-
S-MDM4 mRNA overexpression indicates a poor prognosis and marks a potential therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Cancer Sci. 2012 Dec;103(12):2056-63. doi: 10.1111/cas.12008. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Cancer Sci. 2012. PMID: 22937789 Free PMC article.
-
MDM4 Is Targeted by 1q Gain and Drives Disease in Burkitt Lymphoma.Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 15;79(12):3125-3138. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3438. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31000522
-
MDM4: What do we know about the association between its polymorphisms and cancer?Med Oncol. 2022 Dec 24;40(1):61. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01929-z. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36566308 Review.
-
The long and the short of it: the MDM4 tail so far.J Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Mar 1;11(3):231-244. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz007. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30689920 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Read MDM4 Sequencing Reveals Aberrant Isoform Landscape in Metastatic Melanomas.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 30;25(17):9415. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179415. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273363 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic and teratogenic effects of Trp53Y217C, an inflammation-prone mouse model of the human hotspot mutant TP53Y220C.Elife. 2025 Apr 14;13:RP102434. doi: 10.7554/eLife.102434. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40223808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moretti F. Mdm genes. In: Schwab M, editor. Encyclopedia of cancer. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2017. pp. 2684–2689.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

