The Reelin receptor ApoER2 is a cargo for the adaptor protein complex AP-4: Implications for Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia
- PMID: 38281682
- PMCID: PMC10979513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2024.102575
The Reelin receptor ApoER2 is a cargo for the adaptor protein complex AP-4: Implications for Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "The Reelin receptor ApoER2 is a cargo for the adaptor protein complex AP-4: Implications for hereditary spastic paraplegia" [Progr. Neurobiol. 234(2024)102575].Prog Neurobiol. 2024 Oct;241:102662. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2024.102662. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Prog Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39294072 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
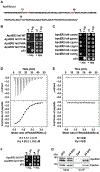
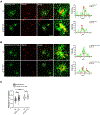
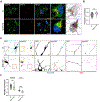
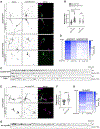
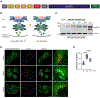
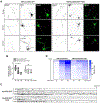
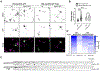
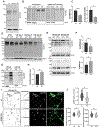
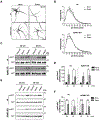
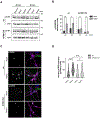
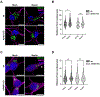
Adaptor protein complex 4 (AP-4) is a heterotetrameric complex that promotes export of selected cargo proteins from the trans-Golgi network. Mutations in each of the AP-4 subunits cause a complicated form of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia (HSP). Herein, we report that ApoER2, a receptor in the Reelin signaling pathway, is a cargo of the AP-4 complex. We identify the motif ISSF/Y within the ApoER2 cytosolic domain as necessary for interaction with the canonical signal-binding pocket of the µ4 (AP4M1) subunit of AP-4. AP4E1- knock-out (KO) HeLa cells and hippocampal neurons from Ap4e1-KO mice display increased co-localization of ApoER2 with Golgi markers. Furthermore, hippocampal neurons from Ap4e1-KO mice and AP4M1-KO human iPSC-derived cortical i3Neurons exhibit reduced ApoER2 protein expression. Analyses of biosynthetic transport of ApoER2 reveal differential post-Golgi trafficking of the receptor, with lower axonal distribution in KO compared to wild-type neurons, indicating a role of AP-4 and the ISSF/Y motif in the axonal localization of ApoER2. Finally, analyses of Reelin signaling in mouse hippocampal and human cortical KO neurons show that AP4 deficiency causes no changes in Reelin-dependent activation of the AKT pathway and only mild changes in Reelin-induced dendritic arborization, but reduces Reelin-induced ERK phosphorylation, CREB activation, and Golgi deployment. This work thus establishes ApoER2 as a novel cargo of the AP-4 complex, suggesting that defects in the trafficking of this receptor and in the Reelin signaling pathway could contribute to the pathogenesis of HSP caused by mutations in AP-4 subunits.
Keywords: AP-4; ApoER2; Golgi; Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia; Neuron; Reelin.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors state that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Update of
-
The Reelin Receptor ApoER2 is a Cargo for the Adaptor Protein Complex AP-4: Implications for Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 22:2023.12.21.572896. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.21.572896. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Prog Neurobiol. 2024 Mar;234:102575. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2024.102575. PMID: 38187774 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Abdollahpour H, Alawi M, Kortum F, Beckstette M, Seemanova E, Komarek V, Rosenberger G and Kutsche K (2015). “An AP4B1 frameshift mutation in siblings with intellectual disability and spastic tetraplegia further delineates the AP-4 deficiency syndrome.” Eur J Hum Genet 23(2): 256–259. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beffert U, Durudas A, Weeber EJ, Stolt PC, Giehl KM, Sweatt JD, Hammer RE and Herz J (2006). “Functional dissection of Reelin signaling by site-directed disruption of Disabled-1 adaptor binding to apolipoprotein E receptor 2: distinct roles in development and synaptic plasticity.” J Neurosci 26(7): 2041–2052. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beffert U, Morfini G, Bock HH, Reyna H, Brady ST and Herz J (2002). “Reelin-mediated signaling locally regulates protein kinase B/Akt and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta.” J Biol Chem 277(51): 49958–49964. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

