The role of mitochondrial DNA copy number in cardiometabolic disease: a bidirectional two-sample mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 38282013
- PMCID: PMC10823732
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-023-02074-1
The role of mitochondrial DNA copy number in cardiometabolic disease: a bidirectional two-sample mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background: This study used a bidirectional 2-sample Mendelian randomization study to investigate the potential causal links between mtDNA copy number and cardiometabolic disease (obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, type 2 diabetes [T2DM], coronary artery disease [CAD], stroke, ischemic stroke, and heart failure).
Methods: Genetic associations with mtDNA copy number were obtained from a genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics from the UK biobank (n = 395,718) and cardio-metabolic disease were from largest available GWAS summary statistics. Inverse variance weighting (IVW) was conducted, with weighted median, MR-Egger, and MR-PRESSO as sensitivity analyses. We repeated this in the opposite direction using instruments for cardio-metabolic disease.
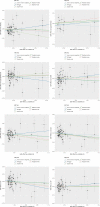
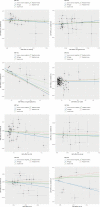
Results: Genetically predicted mtDNA copy number was not associated with risk of obesity (P = 0.148), hypertension (P = 0.515), dyslipidemia (P = 0.684), T2DM (P = 0.631), CAD (P = 0.199), stroke (P = 0.314), ischemic stroke (P = 0.633), and heart failure (P = 0.708). Regarding the reverse directions, we only found that genetically predicted dyslipidemia was associated with decreased levels of mtDNA copy number in the IVW analysis (β= - 0.060, 95% CI - 0.044 to - 0.076; P = 2.416e-14) and there was suggestive of evidence for a potential causal association between CAD and mtDNA copy number (β= - 0.021, 95% CI - 0.003 to - 0.039; P = 0.025). Sensitivity and replication analyses showed the stable findings.
Conclusions: Findings of this Mendelian randomization study did not support a causal effect of mtDNA copy number in the development of cardiometabolic disease, but found dyslipidemia and CAD can lead to reduced mtDNA copy number. These findings have implications for mtDNA copy number as a biomarker of dyslipidemia and CAD in clinical practice.
Keywords: Bidirectional; Cardiometabolic disease; Mitochondrial DNA copy number; Two-sample mendelian randomization study.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NSAD2023047/Nanshan District Health System Science and Technology Major Project
- NS2022009/the Science and Technology Program Key Project of Nanshan District of Shenzhen City
- 82103940/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82073646/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81973152/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82273707/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82373675/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82304228/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022A1515010503/the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2021A1515012503/the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2019B030301009/the Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Regional Immunity and Diseases
- JCYJ20190808145805515/the Science and Technology Development Foundation of Shenzhen
- JCYJ20210324093612032/the Science and Technology Development Foundation of Shenzhen
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

