Comparative genomic analysis of antibiotic resistance and virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients and retail meat
- PMID: 38282615
- PMCID: PMC10811269
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1339339
Comparative genomic analysis of antibiotic resistance and virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients and retail meat
Abstract
Introduction: Staphylococcus aureus is a significant human pathogen that poses a threat to public health due to its association with foodborne contamination and a variety of infections. The factors contributing to the pathogenicity of S. aureus include virulence, drug resistance, and toxin production, making it essential to monitor their prevalence and genetic profiles. This study investigated and compared the genomic characteristics of S. aureus isolates from retail meat and patients in Saudi Arabia.
Methods: A total of 136 S. aureus isolates were obtained between October 2021 and June 2022:84 from patients and 53 from meat samples in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. S. aureus isolates were identified using conventional methods and MALDI-TOF MS, and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) was identified using VITEK2 and BD Phoenix systems. MRSA was confirmed phenotypically using chromogenic agar, and genotypically by detecting mecA. Genomic data were analyzed using BactopiaV2 pipeline, local BLAST, and MLST databases.
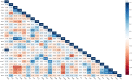
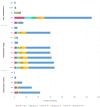
Results: Antibiotic resistance genes were prevalent in both meat and patient S. aureus isolates, with high prevalence of tet38, blaZ, and fosB. Notably, all S. aureus isolates from patients carried multidrug-resistant (MDR) genes, and a high percentage of S. aureus isolates from meat also harbored MDR genes. Phenotypically, 43% of the S. aureus isolates from meat and 100% of the patients' isolates were MDR. Enterotoxin genes, including selX, sem, and sei, exhibited high compatibility between meat and patient S. aureus isolates. Virulence genes such as cap, hly/hla, sbi, and isd were found in all S. aureus isolates from both sources.
Conclusion: Our study established a genetic connection between S. aureus isolates from meat and patients, showing shared antibiotic resistance and virulence genes. The presence of these genes in meat derived isolates underscores its role as a reservoir. Genomic relatedness also suggests potential transmission of resistance between different settings. These findings emphasize the necessity for a comprehensive approach to monitor and control S. aureus infections in both animals and humans.
Keywords: MRSA; Staphylococcal toxins; Staphylococcus aureus; antibiotic resistance genes; virulence factors.
Copyright © 2024 Alkuraythi, Alkhulaifi, Binjomah, Alarwi, Mujallad, Alharbi, Alshomrani, Gojobori and Alajel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genetic Characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus argenteus Isolates Collected in the Dutch National MRSA Surveillance from 2008 to 2021.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0103522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01035-22. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36005448 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, multiple antibiotic resistance and virulence profile of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in retail poultry meat from Edo, Nigeria.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Mar 2;13:1122059. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1122059. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36936767 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, Virulence, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) Strains from Oklahoma Retail Poultry Meats.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 May 29;12(6):6148-61. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120606148. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26035662 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Sep 26;16(9):e70230. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70230. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39463535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential use of toxin antibodies as a strategy for controlling acute Staphylococcus aureus infections.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012 Jun;16(6):601-12. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2012.682573. Epub 2012 Apr 25. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012. PMID: 22530584 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Review of Detection Methods for Staphylococcus aureus and Its Enterotoxins in Food: From Traditional to Emerging Technologies.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jun 23;17(7):319. doi: 10.3390/toxins17070319. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40711131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distribution of Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilm Production Genes in the Genomic Sequences of S. aureus: A Global In Silico Analysis.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Apr 1;14(4):364. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14040364. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298499 Free PMC article.
-
Forecasting the development of antimicrobial resistance of S. aureus.Front Oral Health. 2025 Jan 9;5:1514070. doi: 10.3389/froh.2024.1514070. eCollection 2024. Front Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 39850470 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns and Genes in Staphylococcus aureus From Humans and Animals in Veterinary Clinics Across Thailand.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2025 Jul 21;2025:5541655. doi: 10.1155/tbed/5541655. eCollection 2025. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2025. PMID: 40727307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abulreesh H. H., Organji S. R. (2011). The prevalence of multidrug-resistant staphylococci in food and the environment of Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Res. J. Microbiol. 6 (6), 510–523. doi: 10.3923/jm.2011.510.523 - DOI
-
- Abulreesh H. H., Organji S. R., Osman G. E. H., Elbanna K., Almalki M. H. K., Ahmad I. (2017). Prevalence of antibiotic resistance and virulence factors encoding genes in clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Saudi Arabia. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob Health 5 (4), 196–202. doi: 10.1016/j.cegh.2016.08.004 - DOI
-
- Ahmed B., Mashat B. H. (2014). Prevalence of classical enterotoxin genes in staphylococcus aureus isolated from food handlers in Makkah city kitchens. Asian J. Sci. Tech. 5 (11), 727–731.
-
- Algammal A. M., Hashem M. E. A., Alfifi K. J., Al-Otaibi A. S., Alatawy M., Eltarabili R. M., et al. . (2022. a). Sequence analysis, antibiogram profile, virulence and antibiotic resistance genes of XDR and MDR gallibacterium anatis isolated from layer chickens in Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 15, 4321–4334. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S377797 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

