Tackling strong biofilm and multi-virulent vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus via natural alkaloid-based porous nanoparticles: perspective towards near future eradication
- PMID: 38282617
- PMCID: PMC10811083
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1287426
Tackling strong biofilm and multi-virulent vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus via natural alkaloid-based porous nanoparticles: perspective towards near future eradication
Abstract
Introduction: As a growing direction, nano-based therapy has become a successful paradigm used to address the phytogenic delivery-related problems in overcoming multivirulent vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) infection.
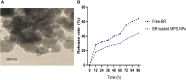
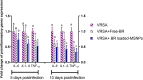
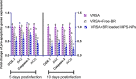
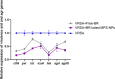
Methods: Hence, our aim was to develop and assess a novel nanocarrier system (mesoporous silica nanoparticles, MPS-NPs) for free berberine (Free-BR) as an antimicrobial alkaloid against strong biofilm-producing and multi-virulent VRSA strains using in vitro and in vivo mouse model.
Results and discussion: Our outcomes demonstrated vancomycin resistance in 13.7% of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) strains categorized as VRSA. Notably, strong biofilm formation was observed in 69.2% of VRSA strains that were all positive for icaA gene. All strong biofilm-producing VRSA strains harbored a minimum of two virulence genes comprising clfA and icaA with 44.4% of them possessing all five virulence genes (icaA, tst, clfA, hla, and pvl), and 88.9% being multi-virulent. The study findings affirmed excellent in vitro antimicrobial and antibiofilm properties of BR-loaded MPS-NPs. Real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) assay displayed the downregulating role of BR-loaded MPS-NPs on strong biofilm-producing and multi-virulent VRSA strains virulence and agr genes in both in vitro and in vivo mice models. Additionally, BR-loaded MPS-NPs supplementation has a promising role in attenuating the upregulated expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines' genes in VRSA-infected mice with attenuation in pro-apoptotic genes expression resulting in reduced VRSA-induced apoptosis. In essence, the current study recommends the future scope of using BR-loaded MPS-NPs as auspicious alternatives for antimicrobials with tremendous antimicrobial, antibiofilm, anti-quorum sensing (QS), and anti-virulence effectiveness against problematic strong biofilm-producing and multi-virulent VRSA-associated infections.
Keywords: QS; VRSA; biofilm; inflammation; multi-virulent; nanoparticles; natural alkaloids.
Copyright © 2024 Abd El-Hamid, Ibrahim, Elazab, Gad, Shalaby, El-Neshwy, Alshahrani, Saif, Algendy, AlHarbi, Saleh, Alharthi and Mohamed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exploring phenotypic and genotypic diversity among methicillin-resistant, vancomycin-resistant, and sensitive Staphylococcus aureus.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 27;103(52):e41051. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041051. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39969287 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ZnO nanoparticles on methicillin, vancomycin, linezolid resistance and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus isolates.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021 Aug 21;20(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12941-021-00459-2. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021. PMID: 34419054 Free PMC article.
-
Surface-functionalized UIO-66-NH2 for dual-drug delivery of vancomycin and amikacin against vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Nov 8;24(1):462. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03615-8. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39516717 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in MRSA and MSSA Isolated from Clinical Samples in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Microb Drug Resist. 2020 Sep;26(9):1071-1080. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0001. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Microb Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32159447
-
Mechanisms of vancomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.J Clin Invest. 2014 Jul;124(7):2836-40. doi: 10.1172/JCI68834. Epub 2014 Jul 1. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24983424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus in Inflammation and Pain: Update on Pathologic Mechanisms.Pathogens. 2025 Feb 12;14(2):185. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14020185. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40005560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Role of Berberine as a Molecular Disruptor in Antimicrobial Strategies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 24;18(7):947. doi: 10.3390/ph18070947. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative unified impact of magnetite iron nanoparticles and quercetin on broiler chickens: performance, antioxidant and immune defense and controlling of Clostridium perfringens infection.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Nov 7;11:1474942. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1474942. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39575436 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting bacterial biofilm-related genes with nanoparticle-based strategies.Front Microbiol. 2024 May 22;15:1387114. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1387114. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38841057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology Meets Phytotherapy: A Cutting-Edge Approach to Treat Bacterial Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 31;26(3):1254. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031254. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941020 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abd El-Hamid M., Bendary M. M. (2013). Association between agr alleles and toxin gene profiles of S. aureus isolates from human and animal sources in Egypt. Int. J. Adv. Res. 1, 133–144. https://www.journalijar.com/article/428/association-between-agr-alleles-....
-
- Abd El-Hamid M. I., Bendary M. (2015). Comparative phenotypic and genotypic discrimination of methicillin resistant and susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in Egypt. Cell Mol. Biol. 61, 101–112. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26429300/. - PubMed
-
- Abd El-Hamid M. I., El-Naenaeey E-s Y., M kandeel T., Hegazy W. A., Mosbah R. A., Nassar M. S., et al. . (2020). Promising antibiofilm agents: Recent breakthrough against biofilm producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus . Antibiotics. 9, 667. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9100667 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alandiyjany M. N., Kishawy A. T., Abdelfattah-Hassan A., Eldoumani H., Elazab S. T., El-Mandrawy S. A., et al. . (2022). Nano-silica and magnetized-silica mitigated lead toxicity: Their efficacy on bioaccumulation risk, performance, and apoptotic targeted genes in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquat Toxicol. 242, 106054. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2021.106054 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

