An overview of recent advances and challenges in predicting compound-protein interaction (CPI)
- PMID: 38282802
- PMCID: PMC10808869
- DOI: 10.1515/mr-2023-0030
An overview of recent advances and challenges in predicting compound-protein interaction (CPI)
Abstract
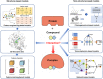
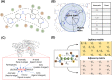
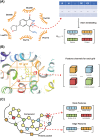
Compound-protein interactions (CPIs) are critical in drug discovery for identifying therapeutic targets, drug side effects, and repurposing existing drugs. Machine learning (ML) algorithms have emerged as powerful tools for CPI prediction, offering notable advantages in cost-effectiveness and efficiency. This review provides an overview of recent advances in both structure-based and non-structure-based CPI prediction ML models, highlighting their performance and achievements. It also offers insights into CPI prediction-related datasets and evaluation benchmarks. Lastly, the article presents a comprehensive assessment of the current landscape of CPI prediction, elucidating the challenges faced and outlining emerging trends to advance the field.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; chemogenomics; compound-protein interaction prediction; drug discovery; scoring function.
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
