Imaging and spatial omics of kidney injury: significance, challenges, advances and perspectives
- PMID: 38282803
- PMCID: PMC10808090
- DOI: 10.1515/mr-2023-0046
Imaging and spatial omics of kidney injury: significance, challenges, advances and perspectives
Abstract
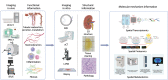
The kidneys are susceptible to a range of insults that can cause damage to them. Early diagnosis, timely prevention, and proper treatment are crucial for improving the outcome of kidney injury. However, the complexity of renal structure and function makes it difficult to reach the demand of early detection and comprehensive evaluation of kidney injury. No successful drug therapy caused by the elaborate pathogenesis mechanism network of kidney injury calls for a systematical interpretation in mechanism researches. Recent advances in renal imaging and omics studies have provided novel views and deeper insights into kidney injury, but also raise challenges in reaching a comprehensive cellular and molecular atlas of kidney injury. Progresses in imaging and omics of kidney injury are being made in various directions, with the initiative of construction a high-resolution structural atlas of kidney, dynamic and non-invasive evaluation of renal function, and systematic establishment of spatially resolved molecular atlas by transcriptomics and metabolomics. With the limitations of a single modality, novel multimodal integration technologies of imaging and omics are being attempted to achieve a systematic description of nephropathy mechanisms. Further extensive efforts in renal multimodal imaging and omics studies are extremely required to deepen our understanding on kidney injury in the context of diagnostic, mechanistic and therapeutic perspectives.
Keywords: imaging; kidney injury; multi-modalities; omics.
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Authors state no conflict of interest. Professor Li Yang is a member of Medical Review editorial board and is not involved in the peer review and decision process of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Bandari J, Fuller TW, Turner RM, D’Agostino LA. Renal biopsy for medical renal disease: indications and contraindications. Can J Urol. 2016;23:8121–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
