Exploratory Study on Micronuclei and Metanuclear Abnormalities in Exfoliated Buccal Cells of COVID-19 Suspected Patients
- PMID: 38282807
- PMCID: PMC10810081
- DOI: 10.4103/joc.joc_53_23
Exploratory Study on Micronuclei and Metanuclear Abnormalities in Exfoliated Buccal Cells of COVID-19 Suspected Patients
Abstract
Context: SARS-CoV-2 virus causes COVID-19 by infecting nasal and oral cavities primarily by attaching its spike proteins to ACE 2 receptors expressed in epithelial cells.
Aim: This study was done to evaluate the micronucleated cell count, metanuclear abnormalities, and genotoxic factor in exfoliated buccal mucosal cell among the COVID-19 suspected patients.
Settings and design: This cross-sectional study was conducted at AIIMS, Mangalagiri, between August and October 2022.
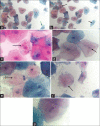
Methods: One hundred COVID-19 suspected patients were recruited for this study after obtaining informed and written consent; buccal smear was obtained and stained for papanicolaou test (PAP). The PAP-stained slides were analyzed for micronuclei (MN), pyknotic, karyolytic, and karyorrhexic cell count, respectively. Based on their reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) report, the patients were grouped into COVID-19 positive and negative groups.
Statistical analysis: The genotoxicity factor was calculated using the micronucleated cell count from both the groups using mean and standard deviation.
Results: The MN, micronucleated cell, pyknotic, karyolitic, and karyorrhexic cell count in COVID-19 positive patients were 24.12, 15.24, 3.08, 2.88 and 4.40, respectively, than COVID-19 negative patients 5.69, 8.17, 1.08, 1.00 and 2.43, respectively. The genotoxicity factor for SARS-CoV-2 was 2.68 which is a positive genotoxic effect on buccal mucosal cells.
Conclusion: SARS-CoV-2 increases the expression of micronucleated cells, pyknotic cells, karyolytic cells, and karyorhexic cells and concludes SARS-CoV-2 is having cytogenotoxic effect on the buccal mucosal cells. This can be used as a reliable marker in identifying the early carcinogenic effects of virus causing COVID-19.
Keywords: Buccal mucosal cells; COVID 19; micronuclei.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Cytology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2022. [[Last accessed on 2022 Oct 24]]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int .
-
- Nakamura T, Hasegawa-Nakamura K, Sakoda K, Matsuyama T, Noguchi K. Involvement of angiotensin II type 1 receptors in interleukin-1b-induced interleukin-6 production in human gingival fibroblasts. Eur J Oral Sci. 2011;119:345–51. - PubMed
-
- Singh S, Saini M, Yadav AS. Elevated frequencies of micronuclei and other nuclear anomalies in alcoholic subjects. J Entomol Zool Stud. 2015;3:243–5.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
