Guggulsterone - a potent bioactive phytosteroid: synthesis, structural modification, and its improved bioactivities
- PMID: 38283224
- PMCID: PMC10809385
- DOI: 10.1039/d3md00432e
Guggulsterone - a potent bioactive phytosteroid: synthesis, structural modification, and its improved bioactivities
Abstract
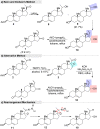
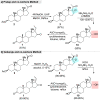
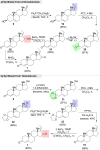
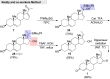
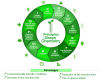
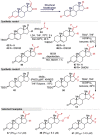
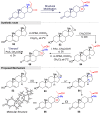
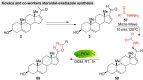
Guggulsterone is a phytosteroid derived from the oleo-gum resin of the critically endangered plant Commiphora wightii. This molecule has attracted increasing attention due to its excellent biochemistry potential and the compound has consequently been evaluated in clinical trials. With a low concentration in natural resources but wide medicinal and therapeutic value, chemists have developed several synthetic routes for guggulsterone starting from various steroid precursors. Moreover, numerous studies have attempted to modify its structure to improve the biological properties. Nowadays, green and sustainable chemistry has also attracted more attention for advanced chemical processes and reactions in steroid chemistry. The present review aimed to summarize the literature and provide an update about the improvements in the chemical synthesis and structural modification of guggulsterone from the view of green chemistry. Moreover, this review encompasses the improved activities of structurally modified guggulsterone derivatives. We expect that the information provided here will be useful to researchers working in this field and on this molecule.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Quantitative determination of guggulsterone in existing natural populations of Commiphora wightii (Arn.) Bhandari for identification of germplasm having higher guggulsterone content.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2015 Jan;21(1):71-81. doi: 10.1007/s12298-014-0271-1. Epub 2014 Nov 22. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2015. PMID: 25648764 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of oleo-gum resin of Commiphora wightii against elastase-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-linked lung inflammation and emphysema: Isolation and identification of key bioactive phytoconstituent.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Oct 5;314:116623. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116623. Epub 2023 May 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37196815
-
Guggulsterone and Its Role in Chronic Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;929:329-361. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41342-6_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27771932 Review.
-
Rising trade, declining stocks: The global gugul (Commiphora wightii) trade.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Sep 15;223:22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.040. Epub 2018 May 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29746995 Review.
-
Guggulsterone from Commiphora mukul potentiates anti-glioblastoma efficacy of temozolomide in vitro and in vivo via down-regulating EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling and NF-κB activation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jan 30;301:115855. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115855. Epub 2022 Oct 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36280019
Cited by
-
Chios Mastic Gum: A Promising Phytotherapeutic for Cardiometabolic Health.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 2;16(17):2941. doi: 10.3390/nu16172941. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating the pharmacological foundations and mechanisms of the Sihai Shuyu formula in treating Graves' disease through integrated serum metabolomics and network pharmacology with molecular docking techniques.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 30;16:1511808. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1511808. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39950029 Free PMC article.
-
Cucurbitacin E Suppresses Adipogenesis and Lipid Accumulation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes Without Cytotoxicity.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 25;13(8):1826. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13081826. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40868081 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Compounds That Target Glioma Stem Cells.NeuroSci. 2025 Jun 5;6(2):52. doi: 10.3390/neurosci6020052. NeuroSci. 2025. PMID: 40559213 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

