COVID-19 in immunocompromised patients after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a pilot study
- PMID: 38283406
- PMCID: PMC10817160
- DOI: 10.1097/BS9.0000000000000183
COVID-19 in immunocompromised patients after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a pilot study
Abstract
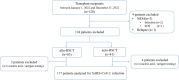
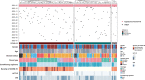
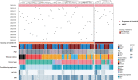
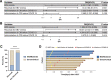
Data on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in patients at early stage of immune reconstitution after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) are limited. In the present study, we retrospectively investigated the incidence and clinical features of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients who underwent HSCT in 2022. Patients (allo-HSCT, n = 80; auto-HSCT, n = 37) were consecutively included in the study. The SARS-CoV-2 infection rate was 59.8%, and the median interval of HSCT to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was 4.8 (range: 0.5-12) months. Most patients were categorized as mild (41.4%) or moderate (38.6%), and 20% as severe/critical. No deaths were attributable to COVID-19. Further analysis showed that lower circulating CD8+ T-cell counts and calcineurin inhibitor administration increased the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Exposure to rituximab significantly increased the probability of severe or critical COVID-19 compared with that of mild/moderate illness (P < .001). In the multivariate analysis, rituximab use was associated with severe COVID-19. Additionally, COVID-19 had no significant effect on immune reconstitution. Furthermore, it was found that Epstein-Barr virus infection and rituximab administration possibly increase the risk of developing severe illness. Our study provides preliminary insights into the effect of SARS-CoV-2 on immune reconstitution and the outcomes of allo-HSCT recipients.
Keywords: Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Immune reconstitution; Immunocompromised patients; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health Inc., on behalf of the Chinese Medical Association (CMA) and Institute of Hematology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College (IHCAMS).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pre-Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Rituximab for Epstein-Barr Virus and Post-Lymphoproliferative Disorder Prophylaxis in Alemtuzumab Recipients.Transplant Cell Ther. 2023 Feb;29(2):132.e1-132.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2022.10.023. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Transplant Cell Ther. 2023. PMID: 36334653
-
Specific immune response to mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 in patients receiving allogeneic stem cell transplantation for myeloid malignancy was altered by immunosuppressive therapy.Leuk Res. 2023 Jul;130:107314. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2023.107314. Epub 2023 May 16. Leuk Res. 2023. PMID: 37216792 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of SARS-CoV-2 in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy Recipients.Transplant Cell Ther. 2021 Sep;27(9):796.e1-796.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2021.07.005. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021. PMID: 34256172 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of COVID-19 in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Transpl Infect Dis. 2022 Apr;24(2):e13792. doi: 10.1111/tid.13792. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Transpl Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35030267
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 in immunocompromised patients: a comprehensive review of coronavirus disease 2019 in hematopoietic stem cell recipients.Curr Opin Crit Care. 2022 Feb 1;28(1):83-89. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000907. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 34813523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization, WHO COVID-19 dashboard, https://covid19.who.int. 2023.
-
- Zhang L, Zhao J, Li R, et al. . Low risk of relapse in aplastic anemia patients after SARS-CoV-2 omicron infection: a prospective NICHE cohort. Am J Hematol 2023;98(10):E272–E275. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
