Monitoring SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load and CD4+ T-cell Count After ART in a Patient Diagnosed With AIDS Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report
- PMID: 38283513
- PMCID: PMC10817777
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.51189
Monitoring SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load and CD4+ T-cell Count After ART in a Patient Diagnosed With AIDS Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report
Abstract
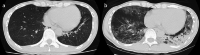
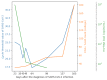
We describe the case of a 36-year-old man diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) following prolonged severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pneumonia. The patient had a complication of pneumocystis pneumonia. Upon initiating highly active antiretroviral therapy, we monitored HIV RNA levels, CD4+ T-cell count, SARS-CoV-2 viral load, and IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. At 167 days post SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis, the patient's CD4+ T-cell count increased to 180 cells/μL. IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 were undetectable despite a decreased SARS-CoV-2 viral load. HIV screening is necessary in cases of prolonged SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia or persistent SARS-CoV-2 shedding. When diagnosed with HIV infection, it is advisable to consider the possibility of pneumocystis pneumonia.
Keywords: acquired immune deficiency syndrome (aids); aids; hiv; pneumocystis pneumonia; sars-cov-2.
Copyright © 2023, Umekage et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIV status is not associated with SARS-CoV-2 viral load and longer duration of infection among people with well-controlled HIV and high COVID-19 vaccine coverage.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 12:2025.05.11.25327398. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.11.25327398. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40463547 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Humoral and Cellular Immune Response Elicited by mRNA Vaccination Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in People Living With Human Immunodeficiency Virus Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy Based on Current CD4 T-Lymphocyte Count.Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 24;75(1):e552-e563. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac238. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35366316 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Evolution and Spike-Specific CD4+ T-Cell Response in Persistent COVID-19 with Severe HIV Immune Suppression.Microorganisms. 2022 Jan 11;10(1):143. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10010143. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35056592 Free PMC article.
-
[Recommendations from the GESIDA/Spanish AIDS Plan regarding antiretroviral treatment in adults with human immunodeficiency virus infection (update February 2009)].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2009 Apr;27(4):222-35. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2008.11.002. Epub 2009 Feb 26. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2009. PMID: 19246124 Spanish.
-
[Consensus document of Gesida and Spanish Secretariat for the National Plan on AIDS (SPNS) regarding combined antiretroviral treatment in adults infected by the human immunodeficiency virus (January 2012)].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2012 Jun;30(6):e1-89. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2012.03.006. Epub 2012 May 23. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2012. PMID: 22633764 Spanish.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality in Headache Disorder Diagnosis, Classification, and Management.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024 Sep;28(9):869-880. doi: 10.1007/s11916-024-01279-7. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024. PMID: 38836996 Review.
References
-
- Immune deficiency is a risk factor for severe COVID-19 in people living with HIV. Hoffmann C, Casado JL, Härter G, et al. HIV Med. 2021;22:372–378. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
