Monitoring SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load and CD4+ T-cell Count After ART in a Patient Diagnosed With AIDS Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report
- PMID: 38283513
- PMCID: PMC10817777
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.51189
Monitoring SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load and CD4+ T-cell Count After ART in a Patient Diagnosed With AIDS Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report
Abstract
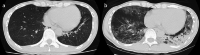
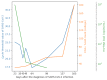
We describe the case of a 36-year-old man diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) following prolonged severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pneumonia. The patient had a complication of pneumocystis pneumonia. Upon initiating highly active antiretroviral therapy, we monitored HIV RNA levels, CD4+ T-cell count, SARS-CoV-2 viral load, and IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. At 167 days post SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis, the patient's CD4+ T-cell count increased to 180 cells/μL. IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 were undetectable despite a decreased SARS-CoV-2 viral load. HIV screening is necessary in cases of prolonged SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia or persistent SARS-CoV-2 shedding. When diagnosed with HIV infection, it is advisable to consider the possibility of pneumocystis pneumonia.
Keywords: acquired immune deficiency syndrome (aids); aids; hiv; pneumocystis pneumonia; sars-cov-2.
Copyright © 2023, Umekage et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Immune deficiency is a risk factor for severe COVID-19 in people living with HIV. Hoffmann C, Casado JL, Härter G, et al. HIV Med. 2021;22:372–378. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
