A systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate blood levels of interleukin-6 in lung cancer patients
- PMID: 38283553
- PMCID: PMC10809806
- DOI: 10.5114/kitp.2023.134177
A systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate blood levels of interleukin-6 in lung cancer patients
Abstract
Introduction: The exact mechanism responsible for inflammation in malignancy is not completely understood, but it is possible that interleukin-6 (IL-6) plays a major role in triggering and maintaining an inflammatory response.
Aim: To conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of the levels of IL-6 in the serum/plasma of lung cancer (LC) patients.
Material and methods: The researchers searched four databases up to September 11, 2022, to find studies that reported on IL-6 levels in LC patients compared to healthy controls (HCs). They calculated effect sizes using standardized mean difference (SMD) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). To evaluate the quality of each study, they used the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS). They performed subgroup analysis, sensitivity analysis, meta-regression analysis, heterogeneity analyses, trial sequential analysis, and publication bias with the trim-and-fill method.
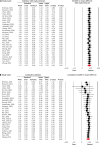
Results: The meta-analysis included 28 studies, and the results showed that the pooled SMD was 1.71 (95% CI: 1.22, 2.19; p < 0.00001; I2 = 98%), indicating that LC patients had significantly higher levels of IL-6 in their serum/plasma than HCs.
Conclusions: The study found that the publication year and quality score of the studies were positively associated with the level of IL-6, while the sample size was inversely related. The research suggests that measuring IL-6 levels in the blood could be useful for detecting and monitoring LC as it appears to be a reliable biomarker.
Keywords: interleukin-6; lung neoplasm; meta-analysis; plasma; serum.
Copyright: © 2023 Polish Society of Cardiothoracic Surgeons (Polskie Towarzystwo KardioTorakochirurgów) and the editors of the Polish Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (Kardiochirurgia i Torakochirurgia Polska).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Elevated levels of interleukin-33 are associated with asthma: A meta-analysis.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Apr;11(4):e842. doi: 10.1002/iid3.842. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37102668 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17 SNPs and serum levels increase ulcerative colitis risk: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 14;20(42):15899-909. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15899. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25400476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-4 expression is increased in patients with tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jun 16;102(24):e34041. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034041. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37327256 Free PMC article.
-
Association between single nucleotide polymorphisms of IL-6 and susceptibility to skin cancer: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Dec;10(12):5110-5122. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1508. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116362 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatokine levels during the first or early second trimester of pregnancy and the subsequent risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Biomarkers. 2021 Sep;26(6):517-531. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2021.1928754. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Biomarkers. 2021. PMID: 34082623
References
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Abate D, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, Abdel-Rahman O, et al. . Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol 2019; 5: 1749-1768. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018; 68: 394-424. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Fedewa SA, Butterly LF, Anderson JC, et al. . Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020; 70: 145-164. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
