Remission of Ectopic Cushing Syndrome Secondary to Medullary Thyroid Cancer With Vandetanib and Selpercatinib
- PMID: 38283729
- PMCID: PMC10821762
- DOI: 10.1210/jcemcr/luad174
Remission of Ectopic Cushing Syndrome Secondary to Medullary Thyroid Cancer With Vandetanib and Selpercatinib
Abstract
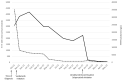
Medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) is a neuroendocrine tumor associated with activating mutations of the rearranged during transfection (RET) proto-oncogene. These tumors may rarely secrete adrenocorticotropin or corticotropin-releasing hormone, resulting in a paraneoplastic ectopic Cushing syndrome (ECS). Paraneoplastic ECS carries a high risk of mortality, and management is difficult due to the lack of response to antiadrenal therapies. We report on a 37-year-old man who was diagnosed with metastatic MTC and reported symptoms of cortisol excess with laboratory testing in keeping with ECS. He began treatment with vandetanib, a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which resulted in decreased tumor burden as well as clinical and biochemical resolution of ECS. Due to progressive structural disease 10 months later, he was switched to the selective RET inhibitor selpercatinib, which was followed by a rapid reduction of cortisol nearing the threshold of adrenal insufficiency. Tumor markers were also improved, and repeat imaging showed decreased tumor burden. Our case highlights the efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the management of paraneoplastic ECS. Selective RET inhibitors may emerge as preferred targeted treatment options due to better efficacy and toxicity profiles compared to multitargeted inhibitors. Clinicians should monitor for adrenal insufficiency with the use of selective RET inhibitors.
Keywords: MTC; RET inhibitors; ectopic Cushing syndrome; medullary thyroid cancer; treatment; tyrosine kinase inhibitors; vandetanib.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures




References
-
- Corsello A, Ramunno V, Locantore P, et al. Medullary thyroid cancer with ectopic Cushing's syndrome: a case report and systematic review of detailed cases from the literature. Thyroid. 2022;32(11):1281‐1298. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
