Antibiotic action and resistance: updated review of mechanisms, spread, influencing factors, and alternative approaches for combating resistance
- PMID: 38283841
- PMCID: PMC10820715
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1305294
Antibiotic action and resistance: updated review of mechanisms, spread, influencing factors, and alternative approaches for combating resistance
Abstract
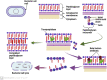
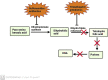
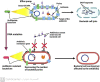
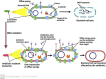
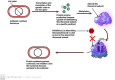
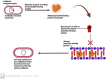
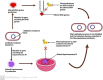
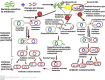
Antibiotics represent a frequently employed therapeutic modality for the management of bacterial infections across diverse domains, including human health, agriculture, livestock breeding, and fish farming. The efficacy of antibiotics relies on four distinct mechanisms of action, which are discussed in detail in this review, along with accompanying diagrammatic illustrations. Despite their effectiveness, antibiotic resistance has emerged as a significant challenge to treating bacterial infections. Bacteria have developed defense mechanisms against antibiotics, rendering them ineffective. This review delves into the specific mechanisms that bacteria have developed to resist antibiotics, with the help of diagrammatic illustrations. Antibiotic resistance can spread among bacteria through various routes, resulting in previously susceptible bacteria becoming antibiotic-resistant. Multiple factors contribute to the worsening crisis of antibiotic resistance, including human misuse of antibiotics. This review also emphasizes alternative solutions proposed to mitigate the exacerbation of antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; antibiotics; antimicrobial; bacteria; disease spreading.
Copyright © 2024 Halawa, Fadel, Al-Rabia, Behairy, Nouh, Abdo, Olga, Fericean, Atwa, El-Nablaway and Abdeen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Benbrook C. M. (2002). Antibiotic drug use in US aquaculture. United States: Institute for Agriculture and Trade Policy Report February, 1–18.
-
- Bhattacharyya S. (2012). Do bacteria age? Resonance 17 (4), 347–364. 10.1007/s12045-012-0037-4 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

