Treadmill Running Regulates Adult Neurogenesis, Spatial and Non-spatial Learning, Parvalbumin Neuron Activity by ErbB4 Signaling
- PMID: 38285192
- PMCID: PMC11407172
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-023-01439-0
Treadmill Running Regulates Adult Neurogenesis, Spatial and Non-spatial Learning, Parvalbumin Neuron Activity by ErbB4 Signaling
Abstract
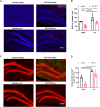
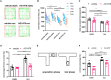
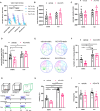
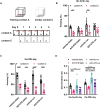
Exercise can promote adult neurogenesis and improve symptoms associated with schizophrenia and other mental disorders via parvalbumin (PV)-positive GABAergic interneurons in the dentate gyrus ErbB4 is the receptor of neurotrophic factor neuregulin 1, expressed mostly in PV-positive interneurons. Whether ErbB4 in PV-positive neurons mediates the beneficial effect of exercise and adult neurogenesis on mental disorder needs to be further investigation. Here, we first conducted a four-week study on the effects of AG1478, an ErbB4 inhibitor, on memory and neurogenesis. AG1478 significantly impaired the performance in several memory tasks, including the T-maze, Morris water maze, and contextual fear conditioning, downregulated the expression of total ErbB4 (T-ErbB4) and the ratio of phosphate-ErbB4 (p-ErbB4) to T-ErbB4, and associated with neurogenesis impairment. Interestingly, AG1478 also appeared to decrease intracellular calcium levels in PV neurons, which could be reversed by exercise. These results suggest exercise may regulate adult neurogenesis and PV neuron activity through ErbB4 signaling. Overall, these findings provide further evidence of the importance of exercise for neurogenesis and suggest that targeting ErbB4 may be a promising strategy for improving memory and other cognitive functions in individuals with mental disorders.
Keywords: AG1478; ErbB4; Fear conditioning; Neurogenesis; Spatial memory; Treadmill running.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ablation of ErbB4 in parvalbumin-positive interneurons inhibits adult hippocampal neurogenesis through down-regulating BDNF/TrkB expression.J Comp Neurol. 2018 Oct 15;526(15):2482-2492. doi: 10.1002/cne.24506. Epub 2018 Oct 17. J Comp Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30329159
-
Parvalbumin Interneuron Activation-Dependent Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Is Required for Treadmill Running to Reverse Schizophrenia-Like Phenotypes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Feb 4;8:24. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00024. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32117963 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation-Induced Downregulation of Hippocampacal Neuregulin 1-ErbB4 Signaling in the Parvalbumin Interneurons Might Contribute to Cognitive Impairment in a Mouse Model of Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy.Inflammation. 2017 Apr;40(2):387-400. doi: 10.1007/s10753-016-0484-2. Inflammation. 2017. PMID: 27913953
-
Inhibitory circuits in fear memory and fear-related disorders.Front Neural Circuits. 2023 Mar 23;17:1122314. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2023.1122314. eCollection 2023. Front Neural Circuits. 2023. PMID: 37035504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuregulin 1: an intriguing therapeutic target for neurodevelopmental disorders.Transl Psychiatry. 2020 Jun 16;10(1):190. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-00868-5. Transl Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32546684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Neurogenesis Promotion Effects between Cinnamoylquinic Acids in Neural Stem Cells from Adult Mice Brains.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Sep 30;15(20):3713-23. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00329. Online ahead of print. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39348888 Free PMC article.
-
Neural stem cell heterogeneity in adult hippocampus.Cell Regen. 2025 Mar 7;14(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13619-025-00222-4. Cell Regen. 2025. PMID: 40053275 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abe Y, Namba H, Zheng Y, Nawa H (2009) In situ hybridization reveals developmental regulation of ErbB1-4 mRNA expression in mouse midbrain: implication of ErbB receptors for dopaminergic neurons. Neuroscience 161:95–110 - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL (2003) Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:517–529 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

