Clinical trials of R-(-)-gossypol (AT-101) in newly diagnosed and recurrent glioblastoma: NABTT 0602 and NABTT 0702
- PMID: 38285688
- PMCID: PMC10824421
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291128
Clinical trials of R-(-)-gossypol (AT-101) in newly diagnosed and recurrent glioblastoma: NABTT 0602 and NABTT 0702
Abstract
Purpose: AT-101 is an oral bcl-2 family protein inhibitor (Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, Mcl-1, Bcl-W) and potent inducer of proapoptotic proteins. A prior study of the parent compound, racemic gossypol, demonstrated objective and durable responses in patients with malignant glioma. AT-101 has demonstrated synergy with radiation in animal models. The objectives of trial NABTT 0602 were to determine the MTD of AT-101 concurrent with temozolomide (TMZ) and radiation therapy (RT) (Arm I) and to determine the MTD of AT-101 when given with adjuvant TMZ after completion of standard chemoradiation (Arm 2). Separately in trial NABTT 0702, the survival and response rates of single agent AT-101 were evaluated in patients with recurrent glioblastoma.
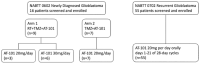
Methods: In NABTT 0602 Phase I, a 3+3 design was used to define MTDs after maximal safe resection, patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma received standard concurrent RT (60 Gy) and TMZ 75 mg/m2/day followed by adjuvant TMZ 150-200 mg/m2 days 1-5 in 28-day cycles (Stupp regimen). In Arm I, AT-101 was administered M-F during the six weeks of RT beginning 20 mg qd. In Arm 2, concurrent with each adjuvant cycle of TMZ, AT-101 was administered at a starting dose of 20 mg, days 1-21 followed by 7-day break for a maximum of 6 cycles. The PK blood samples were collected in the first three patients in each cohort of arm 1. In NABTT 0702 patients with recurrent glioblastoma received 20 mg p.o. per day for 21 of 28 days in repeated cycles to assess overall survival (OS).
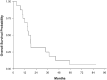
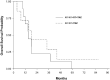
Results: A total of sixteen patients were enrolled on the two study arms of NABTT 0602. In Arm 1 AT-101 was escalated from 20 to 30 mg where one of six patients experienced DLT (grade 3 GI ulcer). On Arm 2 one patient treated at 20 mg experienced DLT (grade 3 ileus, nausea and diarrhea). The cohort was expanded to include seven patients without observation of DLT. PK results were consistent with drug levels from non-CNS studies. At study closure six patients are still alive. The median survival times for Arm I and Arm II are 15.2 months and 18.2 months, respectively. In NABTT 0702 fifty-six patients were enrolled and forty-three were eligible for imaging response. Sixteen patients (29%) had stable disease as best response and one partial response was observed. The median OS with single agent AT-101 was 5.7 months (95%CI: 3.8-7.6 months) for patients with rGBM.
Conclusions: AT-101 can be safely administered with radiation therapy and TMZ in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma without toxicity unique to patients with CNS tumors. Because of toxicity observed in non-CNS AT-101 clinical trials, further dose-escalation was not attempted. The recommended dose for future studies that utilize continual AT-101 exposure is 20 mg days M-F concurrent with RT/TMZ and 20 mg days 1-21 for each 28-day cycle of TMZ. AT-101 has limited activity as a single agent in unselected patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Future trials should attempt to better understand resistance mechanisms and consider combination therapy.
Copyright: © 2024 Fiveash et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phase I study of hypofractionated intensity modulated radiation therapy with concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide in patients with glioblastoma multiforme.Radiat Oncol. 2013 Feb 20;8:38. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-8-38. Radiat Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23425509 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase 1 dose escalation trial of the safety and pharmacokinetics of cabozantinib concurrent with temozolomide and radiotherapy or temozolomide after radiotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with high-grade gliomas.Cancer. 2016 Feb 15;122(4):582-7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29798. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26588662 Clinical Trial.
-
Survival of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated with radiation and temozolomide in research studies in the United States.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Apr 15;16(8):2443-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3106. Epub 2010 Apr 6. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20371685 Free PMC article.
-
Hypofractionated radiotherapy with or without concurrent temozolomide in elderly patients with glioblastoma multiforme: a review of ten-year single institutional experience.J Neurooncol. 2012 Apr;107(2):395-405. doi: 10.1007/s11060-011-0766-3. Epub 2011 Nov 22. J Neurooncol. 2012. PMID: 22105851 Review.
-
Feasibility of preirradiation temozolomide in cases of high-grade gliomas: Our experience and review of literature.J Cancer Res Ther. 2023 Jan-Mar;19(2):221-227. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_942_21. J Cancer Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37006062 Review.
Cited by
-
Lactate's impact on immune cells in sepsis: unraveling the complex interplay.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 20;15:1483400. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1483400. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39372401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical research framework proposal for ketogenic metabolic therapy in glioblastoma.BMC Med. 2024 Dec 5;22(1):578. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03775-4. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 39639257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Approach for Glioblastoma Treatment by Combining Apoptosis Inducers (TMZ, MTX, and Cytarabine) with E.V.A. (Eltanexor, Venetoclax, and A1210477) Inhibiting XPO1, Bcl-2, and Mcl-1.Cells. 2024 Apr 4;13(7):632. doi: 10.3390/cells13070632. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalla NR. Gossypol. Acta Eur Fertil. 1990;21(1):5–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

