Comparative efficacy of terlipressin and norepinephrine for treatment of hepatorenal syndrome-acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38285703
- PMCID: PMC10824429
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296690
Comparative efficacy of terlipressin and norepinephrine for treatment of hepatorenal syndrome-acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
The treatment of choice for hepatorenal syndrome-acute kidney injury (HRS-AKI) is vasoconstrictor therapy in combination with albumin, preferably norepinephrine or terlipressin as recommended by recent guidelines. In the absence of larger head-to-head trials comparing the efficacy of terlipressin and norepinephrine, meta-analysis of smaller studies can provide insights needed to understand the comparative effects of these medications. Additionally, recent changes in the HRS diagnosis and treatment guidelines underscore the need for newer analyses comparing terlipressin and norepinephrine. In this systematic review, we aimed to assess reversal of hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) and 1-month mortality in subjects receiving terlipressin or norepinephrine for the management of HRS-AKI. We searched literature databases, including PubMed, Cochrane, Clinicaltrials.gov, International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, Embase, and ResearchGate, for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published from January 2007 to June 2023 on June 26, 2023. Only trials comparing norepinephrine and albumin with terlipressin and albumin for the treatment of HRS-AKI in adults were included, and trials without HRS reversal as an endpoint or nonresponders were excluded. Pairwise meta-analyses with the random effects model were conducted to estimate odds ratios (ORs) for HRS reversal and 1-month mortality as primary outcomes. Additional outcomes assessed, included HRS recurrence, predictors of response, and incidence of adverse events (AEs). We used the Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool for quality assessment. We included 7 RCTs with a total of 376 subjects with HRS-AKI or HRS type 1. This meta-analysis showed numerically higher rates of HRS reversal (OR 1.33, 95% confidence interval [CI] [0.80-2.22]; P = 0.22) and short-term survival (OR 1.50, 95% CI [0.64-3.53]; P = 0.26) with terlipressin, though these results did not reach statistical significance. Terlipressin was associated with AEs such as abdominal pain and diarrhea, whereas norepinephrine was associated with cardiovascular AEs such as chest pain and ischemia. Most of the AEs were reversible with a reduction in dose or discontinuation of therapy across both arms. Of the terlipressin-treated subjects, 5.3% discontinued therapy due to serious AEs compared to 2.7% of the norepinephrine-treated subjects. Limitations of this analysis included small sample size and study differences in HRS-AKI diagnostic criteria. As more studies using the new HRS-AKI criteria comparing terlipressin and norepinephrine are completed, a clearer understanding of the comparability of these 2 therapies will emerge.
Copyright: © 2024 Olson, Subramanian. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
Both JCO and RMS have served as consultants for Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals related to terlipressin. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products associated with this research to declare.
Figures
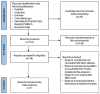


Similar articles
-
Hepatorenal Syndrome With Acute Kidney Injury: Diagnosis and Medical Management.Ann Pharmacother. 2024 Feb;58(2):156-164. doi: 10.1177/10600280231177698. Epub 2023 Jun 4. Ann Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 37271967 Review.
-
Terlipressin versus norepinephrine in the treatment of hepatorenal syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 9;9(9):e107466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107466. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25203311 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment-Related Cost Analysis of Terlipressin for Adults with Hepatorenal Syndrome with Rapid Reduction in Kidney Function.Adv Ther. 2023 Dec;40(12):5432-5446. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02674-z. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 37812332 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy of vasoconstrictor therapies for type 1 hepatorenal syndrome: a network meta-analysis.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Nov;11(11):1009-1018. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2017.1356223. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28708431 Review.
-
Limited Progress in Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS) Reversal and Survival 2002-2018: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Dig Dis Sci. 2020 May;65(5):1539-1548. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05858-2. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Dig Dis Sci. 2020. PMID: 31571102 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Terlipressin versus placebo or noradrenalin in the treatment of hepatorenal syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 4;15:1418826. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1418826. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39295934 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and type of adverse events in patients with cirrhosis receiving terlipressin: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Hepatol Commun. 2024 Sep 18;8(10):e0526. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000526. eCollection 2024 Oct 1. Hepatol Commun. 2024. PMID: 39298544 Free PMC article.
-
The current applications and future directions of terlipressin.Hepatol Commun. 2025 Apr 3;9(4):e0685. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000685. eCollection 2025 Apr 1. Hepatol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40178480 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Biggins SW, Angeli P, Garcia‐Tsao G, Gines P, Ling SC, Nadim MK, et al.. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and hepatorenal syndrome: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2021;74(2):1014–1048. doi: 10.1002/hep.31884 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

