The Effects of ABT-199 and Dihydroartemisinin Combination on Cell Growth and Apoptosis in Human U937 and KG-1 Cancer Cells
- PMID: 38285802
- PMCID: PMC10911724
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.1.343
The Effects of ABT-199 and Dihydroartemisinin Combination on Cell Growth and Apoptosis in Human U937 and KG-1 Cancer Cells
Abstract
Introduction: Change in the balance of Bcl-2 family proteins is one of the main reasons for resistance of tumor cells to ABT-199. In this study, the effect of dihydroartemisinin on cell growth, apoptosis and sensitivity of the AML cells to ABT-199 was investigated.
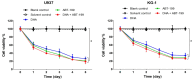
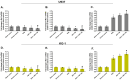
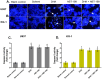
Methods: Cell proliferation and survival were assessed by trypan blue staining and MTT assay, respectively. Cell apoptosis was measured by Hoechst 33342 staining and caspase-3 activity assay. The expression levels of Bcl-2, Mcl-1 and Bax mRNA were tested by qRT-PCR.
Results: Our data showed that combination therapy significantly reduced the IC50 value and synergistically decreased the AML cell survival and growth compared with dihydroartemisinin or ABT-199 alone. Treatment with each of ABT-199 or dihydroartemisinin alone clearly enhanced the Bax mRNA expression and inhibited the expression of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 mRNA. Inhibition of Mcl-1 mRNA by dihydroartemisinin was associated with enhancement of apoptosis induced by ABT-199 in AML cells.
Conclusion: In conclusion, dihydroartemisinin not only triggers the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis, but also can increase the sensitivity of the AML cells to ABT-199 via suppression of Mcl-1 expression.
Keywords: ABT-199; AML; Apoptosis; Bcl-2; dihydroartemisinin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dihydroartemisinin Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of BH3 Mimetic Inhibitor in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells via Inhibition of Mcl-1.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Jan 1;25(1):325-332. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.1.325. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 38285800 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of XPO1 enhances cell death induced by ABT-199 in acute myeloid leukaemia via Mcl-1.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Dec;22(12):6099-6111. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13886. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30596398 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of elevated anti-apoptotic MCL-1 and BCL-2 on the development and treatment of MLL-AF9 AML in mice.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Jul;26(7):1316-1331. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0209-1. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30470795 Free PMC article.
-
The Bcl-2/xL inhibitor ABT-263 increases the stability of Mcl-1 mRNA and protein in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Mol Cancer. 2014 Apr 30;13:98. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-98. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24779770 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of CHK1 enhances cell death induced by the Bcl-2-selective inhibitor ABT-199 in acute myeloid leukemia cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):34785-99. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9185. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27166183 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A combination of Dihydroartemisinin and Venetoclax enhances antitumor effect in AML via C-MYC/BCL-XL/MCL-1 triple targeting.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 9;16(1):496. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02242-7. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40202582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lauria F, Raspadori D, Rondelli D, Ventura MA, Fiacchini M, Visani G, et al. High bcl-2 expression in acute myeloid leukemia cells correlates with cd34 positivity and complete remission rate. Leukemia. 1997;11(12):2075–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

